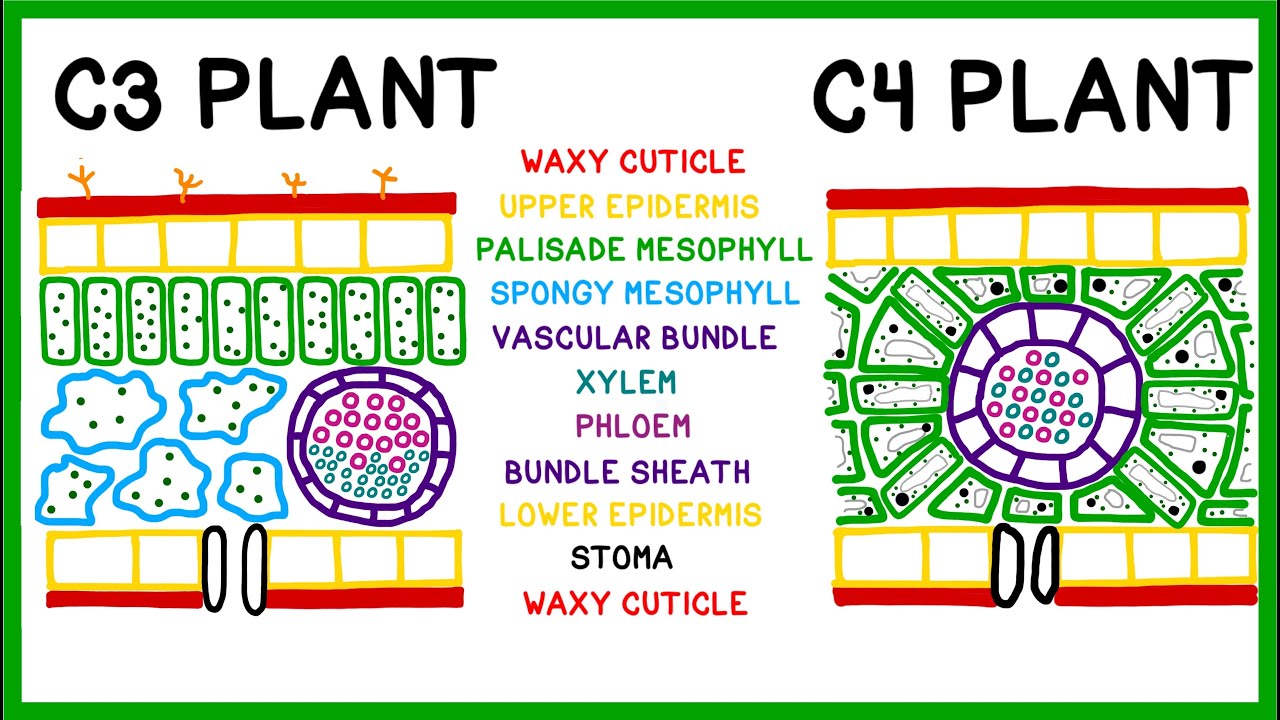
What are C3 plants? C3 plants are a type of plant that uses the C3 carbon fixation pathway, the most common photosynthetic process. This pathway is named after the three-carbon molecule, 3-phosphoglycerate, produced during the first step of the Calvin cycle. Why are they important? These plants are crucial because they make up about 85% of all plant species, including many of our staple crops like rice, wheat, and soybeans. How do they differ from other plants? Unlike C4 and CAM plants, C3 plants thrive in cooler, wetter climates and are less efficient in hot, dry conditions. Want to know more? Here are 28 fascinating facts about C3 plants that will help you understand their role in our ecosystem and agriculture.
What Are C3 Plants?
C3 plants are a type of plant that uses the C3 carbon fixation pathway as the first step in photosynthesis. This process is named after the three-carbon compound, 3-phosphoglycerate, which is produced. These plants are incredibly common and include many of the crops we rely on daily.
-
C3 plants make up about 85% of all plant species. This includes many of the world's most important crops like wheat, rice, and soybeans.
-
They thrive in cooler, wetter climates. C3 plants are more efficient in environments where temperatures are moderate and water is abundant.
-
The first product of carbon fixation in C3 plants is a three-carbon molecule. This molecule is called 3-phosphoglycerate.
Photosynthesis in C3 Plants
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy. C3 plants have a unique way of doing this, which sets them apart from other types of plants.
-
C3 photosynthesis is the most common form of photosynthesis. It occurs in the majority of plants on Earth.
-
C3 plants use the enzyme RuBisCO for carbon fixation. RuBisCO is the most abundant enzyme on the planet.
-
They are less efficient in hot, dry conditions. In such environments, C3 plants can lose a lot of water through a process called photorespiration.
Examples of C3 Plants
Many of the plants we encounter daily are C3 plants. These plants are essential for food production and various other uses.
-
Wheat is a C3 plant. It is one of the most widely grown crops in the world.
-
Rice, another staple food, is also a C3 plant. It feeds more than half of the world's population.
-
Soybeans, used for oil and protein, are C3 plants. They are a major source of animal feed and human food.
Advantages and Disadvantages
C3 plants have their pros and cons, especially when compared to other types of plants like C4 and CAM plants.
-
C3 plants are more efficient in cooler climates. They can photosynthesize more effectively when temperatures are lower.
-
They are less efficient in hot, dry climates. High temperatures can cause them to lose water and energy through photorespiration.
-
C3 plants require more water. They need a consistent water supply to thrive, making them less suitable for arid regions.
Evolution of C3 Plants
The evolution of C3 plants is a fascinating topic that sheds light on how these plants have adapted over millions of years.
-
C3 plants evolved around 400 million years ago. They were among the first plants to colonize land.
-
They have adapted to a wide range of environments. From temperate forests to grasslands, C3 plants are incredibly versatile.
-
C3 plants have a simpler photosynthetic pathway. This simplicity makes them more adaptable to various conditions.
C3 Plants and Agriculture
C3 plants play a crucial role in agriculture, providing food, fiber, and other essential resources.
-
Wheat and rice are staple foods for billions of people. These C3 plants are vital for global food security.
-
Soybeans are a major source of protein and oil. They are used in countless food products and animal feeds.
-
C3 plants are often used in crop rotation. This practice helps maintain soil health and fertility.
Environmental Impact
C3 plants have a significant impact on the environment, both positive and negative.
-
C3 plants contribute to carbon sequestration. They absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, helping to mitigate climate change.
-
They can be affected by climate change. Rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns can impact their growth and productivity.
-
C3 plants are sensitive to air pollution. Pollutants like ozone can reduce their photosynthetic efficiency.
Future of C3 Plants
The future of C3 plants is closely tied to advancements in agricultural practices and climate change mitigation.
-
Genetic engineering could improve C3 plant efficiency. Scientists are working on ways to make these plants more resilient to heat and drought.
-
Sustainable farming practices can benefit C3 plants. Techniques like no-till farming and cover cropping can improve soil health and water retention.
-
Climate change poses a challenge for C3 plants. Rising temperatures and extreme weather events could threaten their productivity.
Fun Facts About C3 Plants
Here are some interesting tidbits about C3 plants that you might not know.
-
The majority of houseplants are C3 plants. They thrive in the moderate conditions found indoors.
-
C3 plants can be found on every continent. From the Arctic tundra to tropical rainforests, they are incredibly diverse.
-
Some of the world's oldest trees are C3 plants. Bristlecone pines, which can live for thousands of years, are an example.
-
C3 plants are essential for the production of many beverages. Coffee, tea, and beer all come from C3 plants.
Final Thoughts on C3 Plants
C3 plants are fascinating. They make up about 85% of all plant species, including wheat, rice, and soybeans. These plants use the Calvin cycle for photosynthesis, which is efficient in cool, wet climates. However, they struggle in hot, dry conditions due to photorespiration, where oxygen competes with carbon dioxide, reducing their efficiency.
Understanding C3 plants helps us appreciate their role in agriculture and ecosystems. They’re crucial for food production and carbon cycling. With climate change, studying these plants becomes even more important. Scientists are exploring ways to improve their resilience and efficiency.
In short, C3 plants are vital to our world. They feed us, support ecosystems, and play a key role in the carbon cycle. By learning about them, we can better protect and utilize these essential plants.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
