Rb protein, also known as retinoblastoma protein, plays a crucial role in regulating the cell cycle. But what exactly does it do? This protein acts as a tumor suppressor, meaning it helps prevent cells from growing uncontrollably, which can lead to cancer. Mutations in the Rb protein can result in serious health issues, including retinoblastoma, a rare type of eye cancer in children. Understanding the functions and importance of Rb protein can shed light on how our bodies control cell growth and maintain health. Ready to learn more? Let's dive into 27 fascinating facts about this essential protein.
What is Rb Protein?
The Rb protein, or retinoblastoma protein, plays a crucial role in regulating the cell cycle. It acts as a tumor suppressor, preventing cells from dividing uncontrollably. Understanding this protein can offer insights into cancer research and treatment.
- Rb protein was first discovered in 1986 by researchers studying retinoblastoma, a rare eye cancer in children.
- It is encoded by the RB1 gene, located on chromosome 13.
- The protein helps control the transition from the G1 phase to the S phase in the cell cycle.
- Mutations in the RB1 gene can lead to various cancers, including retinoblastoma, osteosarcoma, and bladder cancer.
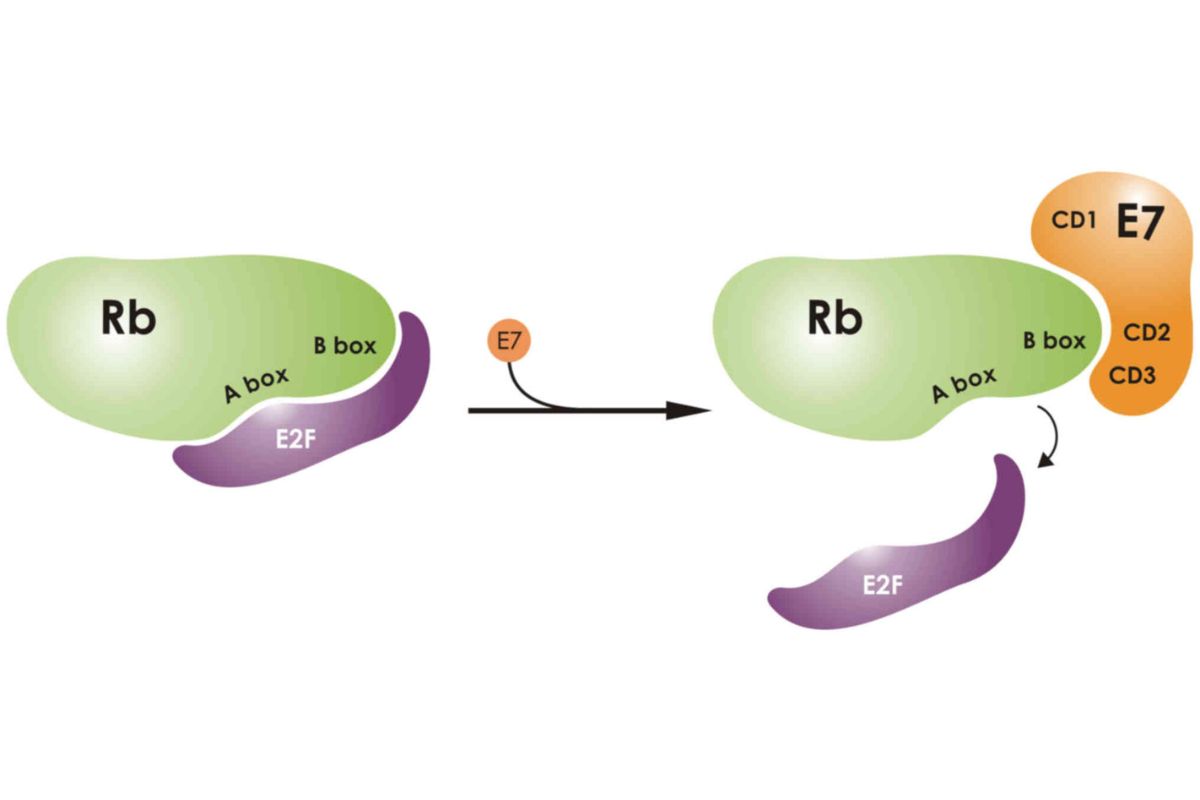
- Rb protein interacts with E2F transcription factors to regulate gene expression.
- When Rb protein is phosphorylated, it becomes inactive, allowing cell cycle progression.
- In its active form, Rb protein binds to E2F, preventing it from activating genes needed for DNA replication.
Functions of Rb Protein
The Rb protein has several essential functions in the body, particularly in cell cycle regulation and tumor suppression. Here are some key roles it plays:
- It acts as a checkpoint in the cell cycle, ensuring cells do not divide uncontrollably.
- Rb protein helps maintain genomic stability by preventing DNA damage.
- It plays a role in cellular differentiation, helping cells develop into their specialized forms.
- The protein can induce cell cycle arrest in response to DNA damage, allowing time for repair.
- Rb protein is involved in apoptosis, or programmed cell death, which removes damaged or unnecessary cells.
- It also regulates senescence, a state where cells stop dividing but remain metabolically active.
- Rb protein interacts with various other proteins, including histone deacetylases and chromatin remodeling complexes, to control gene expression.
Rb Protein and Cancer
Mutations in the RB1 gene and dysfunction of the Rb protein are closely linked to cancer development. Here are some facts about this connection:
- Retinoblastoma, a childhood eye cancer, is directly caused by mutations in the RB1 gene.
- Rb protein dysfunction is found in many types of cancers, including lung, breast, and prostate cancers.
- Loss of Rb protein function can lead to uncontrolled cell division and tumor formation.
- Rb protein mutations are often accompanied by other genetic changes that promote cancer progression.
- Researchers are exploring therapies that target the Rb protein pathway to treat cancer.
- Restoring Rb protein function in cancer cells can potentially halt tumor growth.
- Rb protein status is sometimes used as a biomarker to predict cancer prognosis and treatment response.
Research and Therapeutic Implications
Ongoing research on the Rb protein continues to reveal new insights and potential therapeutic applications. Here are some recent findings and future directions:
- Scientists are studying how Rb protein interacts with other tumor suppressors, like p53, to develop combination therapies.
- Gene therapy approaches aim to correct RB1 gene mutations in retinoblastoma patients.
- Small molecules that mimic Rb protein function are being tested as potential cancer treatments.
- Researchers are investigating how Rb protein dysfunction contributes to resistance to chemotherapy and radiation.
- Understanding the role of Rb protein in stem cell biology could lead to new regenerative medicine strategies.
- Advances in CRISPR technology offer the possibility of precisely editing the RB1 gene to restore normal Rb protein function.
Final Thoughts on Rb Protein
Rb protein plays a crucial role in regulating cell growth and preventing cancer. It acts as a tumor suppressor, ensuring cells don't divide uncontrollably. Mutations in the Rb gene can lead to retinoblastoma, a rare eye cancer in children. Understanding Rb protein's function helps researchers develop better cancer treatments.
Scientists continue to study Rb protein to unlock more secrets about its role in cell cycle control. This knowledge could lead to breakthroughs in cancer therapy and prevention. The more we learn about Rb protein, the better equipped we'll be to combat various cancers.
Stay curious and keep exploring the fascinating world of cellular biology. Every fact you learn brings us one step closer to a healthier future.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
