Negative feedback is a term often heard in science, engineering, and even everyday conversations. But what exactly does it mean? Negative feedback is a process where a system responds to a change by returning to its original state or by decreasing the rate at which the change is occurring. This concept is crucial in various fields, from biology to electronics. For instance, in biology, it helps maintain homeostasis, keeping our bodies stable. In electronics, it stabilizes amplifiers and other circuits. Understanding negative feedback can help you grasp how systems self-regulate and maintain balance. Ready to dive into 27 fascinating facts about negative feedback? Let's get started!
What is Negative Feedback?
Negative feedback is a process where a system responds to a change by returning to its original state or by decreasing the rate at which the change is occurring. This concept is widely used in various fields, including biology, engineering, and social sciences. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about negative feedback.
-
Homeostasis in Biology
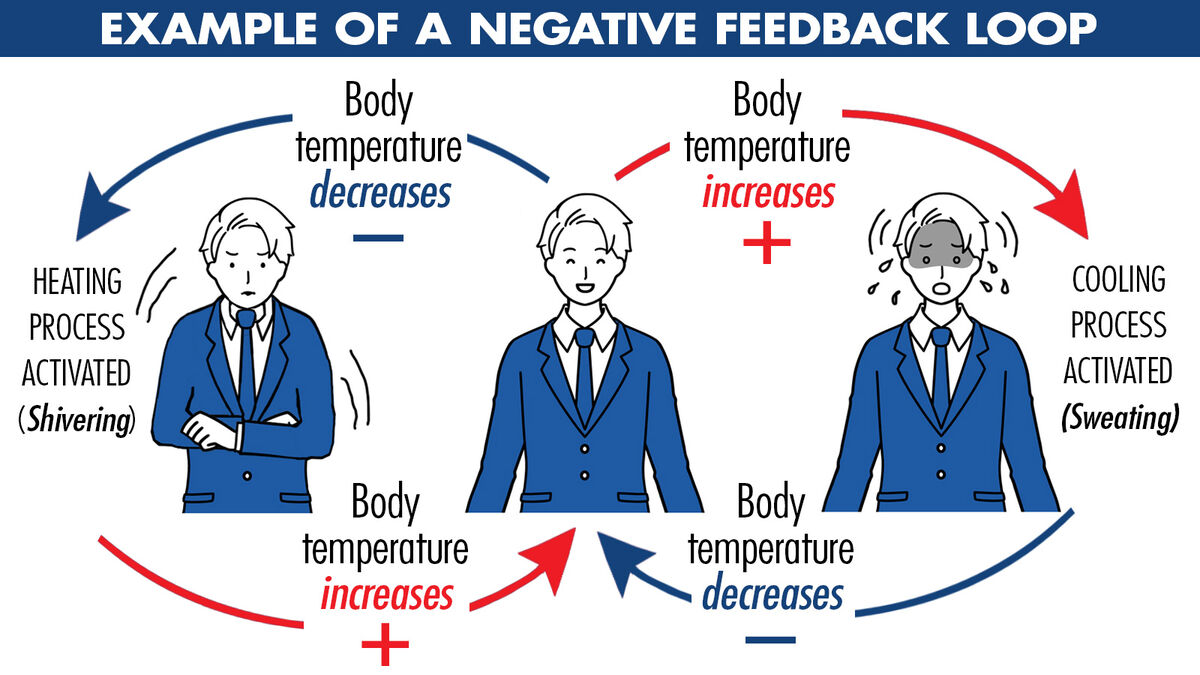
Negative feedback helps maintain homeostasis in living organisms. For example, when body temperature rises, mechanisms like sweating are triggered to cool it down. -
Thermostats Use It
Thermostats in homes use negative feedback to maintain a set temperature. When the room gets too hot, the thermostat turns off the heater. -
Hormonal Regulation
The endocrine system uses negative feedback to regulate hormone levels. For instance, high blood sugar triggers insulin release, which lowers blood sugar levels. -
Audio Systems
In audio systems, negative feedback reduces distortion and improves sound quality. It helps in maintaining the fidelity of the audio signal. -
Economic Stability
Economies use negative feedback mechanisms to stabilize markets. Interest rate adjustments by central banks are a prime example.
Negative Feedback in Engineering
Engineering systems often rely on negative feedback to ensure stability and performance. Here are some intriguing examples:
-
Cruise Control in Cars
Cruise control systems use negative feedback to maintain a constant speed. When the car slows down, the system increases throttle to speed up. -
Amplifiers
Electronic amplifiers use negative feedback to control gain and reduce noise, ensuring a clear output signal. -
Robotics
Robots use negative feedback loops to correct their movements, ensuring precise and accurate operations. -
Aircraft Autopilot
Autopilot systems in aircraft use negative feedback to maintain a set course and altitude, adjusting controls as needed. -
Industrial Automation
Negative feedback is crucial in industrial automation for maintaining process variables like temperature, pressure, and flow rates.
Social and Psychological Aspects
Negative feedback isn't just for machines and biology; it plays a role in social and psychological contexts too.
-
Behavioral Correction
Negative feedback is used in behavioral psychology to reduce undesirable behaviors. For example, a child might receive a timeout for misbehaving. -
Performance Reviews
In workplaces, negative feedback during performance reviews helps employees improve their skills and work habits. -
Social Interactions
Negative feedback in social interactions can help individuals adjust their behavior to fit social norms and expectations. -
Learning and Education
Teachers use negative feedback to correct students' mistakes, helping them learn and improve. -
Self-Regulation
Individuals use negative feedback to self-regulate behaviors, such as dieting or exercising to achieve personal goals.
Environmental and Ecological Impacts
Negative feedback mechanisms also play a crucial role in environmental and ecological systems.
-
Climate Regulation
Earth's climate system uses negative feedback to regulate temperature. For example, increased cloud cover can reflect sunlight, cooling the planet. -
Population Control
In ecosystems, negative feedback helps control population sizes. Predation and resource availability are factors that keep populations in check. -
Carbon Cycle
The carbon cycle involves negative feedback mechanisms that regulate atmospheric CO2 levels, affecting global temperatures. -
Water Cycle
The water cycle uses negative feedback to maintain balance. Evaporation and precipitation rates adjust to keep water levels stable. -
Soil Erosion
Vegetation acts as a negative feedback mechanism to prevent soil erosion by stabilizing the soil with roots.
Technological Applications
Negative feedback is integral to many technological advancements and applications.
-
Internet Algorithms
Algorithms on the internet, like those used by search engines, use negative feedback to improve accuracy and relevance of search results. -
Medical Devices
Medical devices, such as insulin pumps, use negative feedback to regulate and administer the correct dosage of medication. -
Climate Control Systems
Modern climate control systems in buildings use negative feedback to maintain comfortable indoor environments. -
Smartphones
Smartphones use negative feedback in various sensors to adjust screen brightness, volume, and other settings automatically. -
Gaming Consoles
Gaming consoles use negative feedback to enhance user experience, such as adjusting difficulty levels based on player performance. -
Wearable Technology
Wearable devices, like fitness trackers, use negative feedback to monitor and provide feedback on physical activity and health metrics. -
Renewable Energy Systems
Renewable energy systems, such as wind turbines and solar panels, use negative feedback to optimize energy production and efficiency.
The Power of Negative Feedback
Negative feedback isn't just criticism. It’s a tool for growth. When used right, it can lead to improvement, innovation, and stronger relationships. Embracing constructive criticism helps individuals and organizations identify weaknesses and turn them into strengths. It’s not about pointing out flaws but about fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
Remember, feedback should be specific, actionable, and delivered with empathy. This approach ensures the recipient understands the intent and can make meaningful changes. Whether in personal relationships, workplaces, or creative endeavors, negative feedback, when given and received properly, can be a catalyst for positive change.
So next time you receive or give feedback, think of it as a stepping stone to betterment. Embrace it, learn from it, and watch how it transforms your world.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
