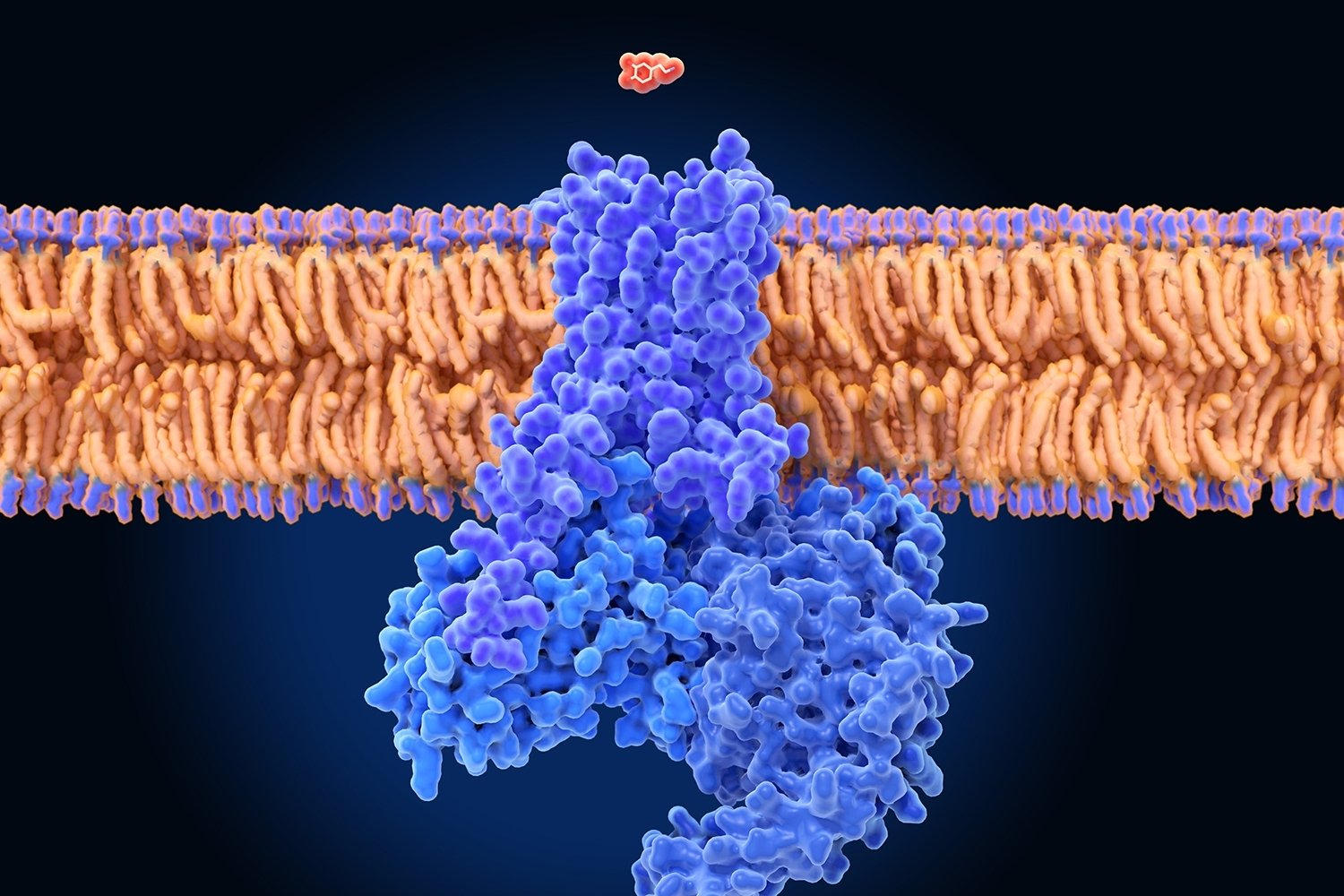
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are fascinating molecules that play a crucial role in how our bodies function. These receptors are involved in many physiological processes, from how we perceive light and taste to how our hearts beat. GPCRs are a large family of proteins that sit on cell surfaces, acting as gatekeepers that transmit signals from the outside world into the cell. They are essential for our senses, immune responses, and even our mood. Understanding these receptors can help in developing new medications for various diseases, including cancer, heart disease, and mental health disorders. Dive into these 27 facts to learn more about the incredible world of G protein-coupled receptors.
What are G protein-coupled receptors?
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are a large family of cell surface receptors that play a crucial role in transmitting signals from outside the cell to the inside. They are involved in many physiological processes and are a major target for drug development.
- GPCRs are also known as seven-transmembrane receptors because they span the cell membrane seven times.
- They are the largest family of cell surface receptors, with over 800 different types identified in humans.
- GPCRs are involved in a wide range of functions, including vision, taste, smell, and neurotransmission.
- These receptors can detect molecules outside the cell and activate internal signal transduction pathways and cellular responses.
- GPCRs are activated by a variety of ligands, including hormones, neurotransmitters, and light-sensitive compounds.
How do GPCRs work?
Understanding the mechanism of GPCRs can help in developing drugs that target these receptors more effectively. Here's a closer look at how they function.
- When a ligand binds to a GPCR, it causes a conformational change in the receptor.
- This change allows the GPCR to interact with a G protein, which is located on the inside of the cell membrane.
- The G protein is then activated and can influence various intracellular signaling pathways.
- GPCRs can activate multiple signaling pathways, leading to diverse cellular responses.
- The signaling pathways activated by GPCRs can result in changes in gene expression, enzyme activity, and ion channel function.
Importance of GPCRs in Medicine
GPCRs are a major target for drug development due to their involvement in many diseases. Here are some key facts about their medical significance.
- Approximately 34% of all FDA-approved drugs target GPCRs.
- Drugs that target GPCRs are used to treat a wide range of conditions, including hypertension, asthma, and depression.
- GPCRs are involved in the action of many over-the-counter medications, such as antihistamines and decongestants.
- Some of the most well-known drugs that target GPCRs include beta-blockers, which are used to treat high blood pressure, and opioids, which are used for pain relief.
- Research into GPCRs has led to the development of new drugs that are more selective and have fewer side effects.
GPCRs in Sensory Perception
GPCRs play a crucial role in our senses, including vision, taste, and smell. Here's how they contribute to sensory perception.
- In vision, GPCRs are involved in the detection of light by photoreceptor cells in the retina.
- The GPCR rhodopsin is responsible for the initial step in the perception of light.
- In taste, GPCRs are involved in detecting sweet, bitter, and umami flavors.
- GPCRs in the olfactory system are responsible for detecting a wide range of odors.
- Mutations in GPCRs can lead to sensory disorders, such as color blindness and anosmia (loss of smell).
GPCRs and Disease
GPCRs are implicated in many diseases, making them important targets for therapeutic intervention. Here are some facts about their role in disease.
- Mutations in GPCRs can lead to a variety of genetic disorders, including retinitis pigmentosa and congenital hypothyroidism.
- GPCRs are involved in the development and progression of cancer, making them targets for cancer therapy.
- In cardiovascular disease, GPCRs play a role in regulating heart rate and blood pressure.
- GPCRs are also involved in metabolic disorders, such as diabetes and obesity.
- Research into GPCRs has led to the identification of new therapeutic targets for a variety of diseases.
Future of GPCR Research
The study of GPCRs continues to be a dynamic field with many exciting developments on the horizon. Here are some future directions for GPCR research.
- Advances in structural biology are providing new insights into the structure and function of GPCRs.
- The development of new technologies, such as cryo-electron microscopy, is allowing researchers to study GPCRs in greater detail.
The Final Word on G Protein-Coupled Receptors
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are vital for many bodily functions. They play a key role in how cells respond to external signals, impacting everything from vision to taste. Understanding GPCRs can lead to breakthroughs in treating diseases like cancer, diabetes, and heart conditions. These receptors are also a hot topic in drug development, with many medications targeting them to improve health outcomes.
Research continues to uncover new aspects of GPCRs, making them an exciting area of study. Their versatility and importance can't be overstated. Whether you're a student, a scientist, or just curious, knowing about GPCRs opens up a world of fascinating information. Keep an eye on this field; it's bound to bring more surprises and advancements in the future.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
