Ever wondered why blood transfusions require matching blood types? The ABO blood group system, discovered by Karl Landsteiner in 1901, is crucial for safe transfusions. Blood types—A, B, AB, and O—are determined by the presence or absence of antigens on red blood cells. These antigens trigger immune responses if foreign blood is introduced. For instance, Type A blood has A antigens and anti-B antibodies, while Type O lacks A and B antigens but has both antibodies. Understanding these differences can save lives. Did you know Type O negative is the universal donor? This means it can be given to anyone in emergencies. Dive into these 27 fascinating facts about ABO blood groups to learn more!
What Are ABO Blood Groups?
The ABO blood group system is one of the most important classifications of human blood. It determines compatibility for blood transfusions and organ transplants. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about this essential system.
-
The ABO blood group system was discovered by Karl Landsteiner in 1901. He identified the A, B, and O blood types, which revolutionized medical science.
-
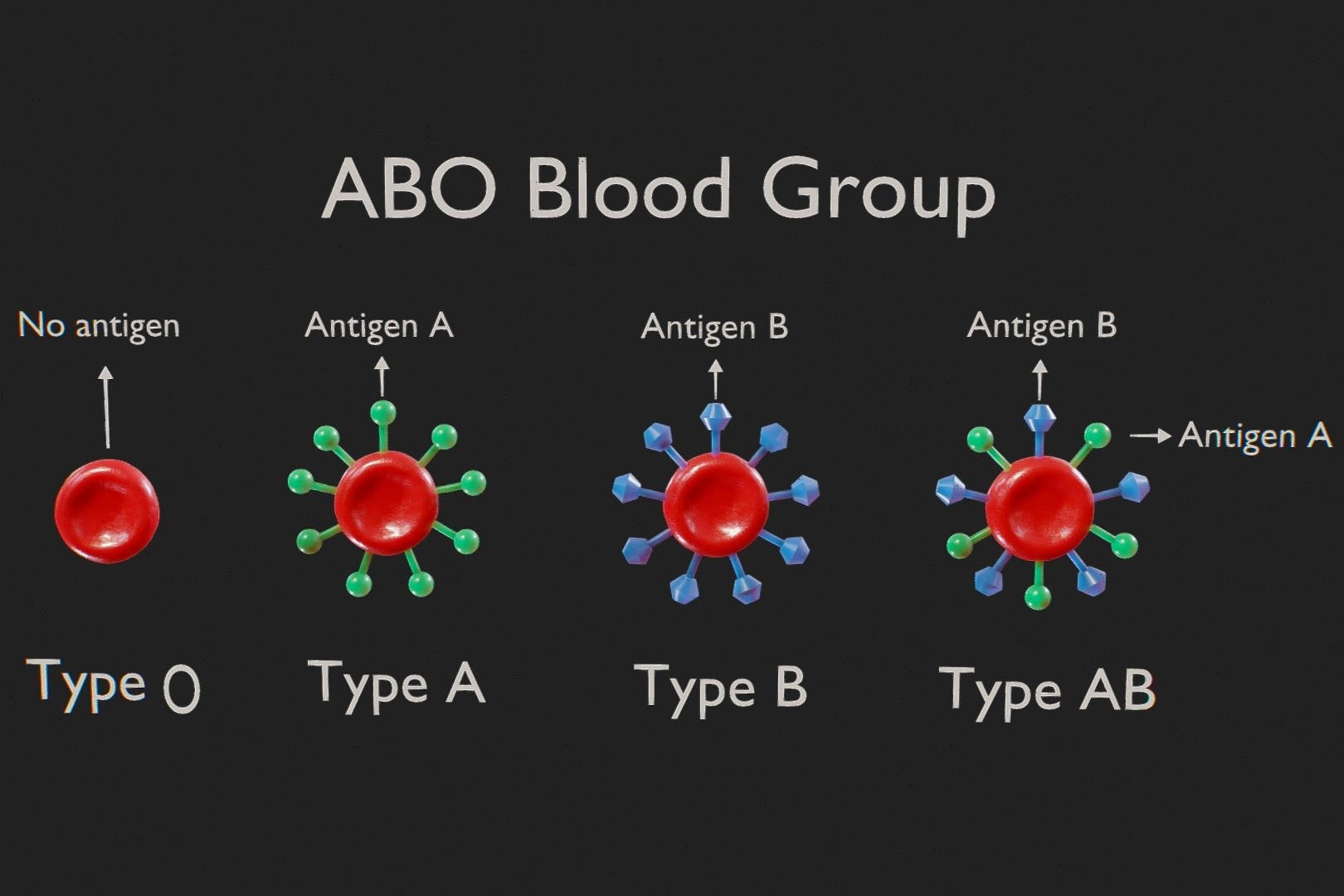
Blood type is determined by the presence or absence of antigens on the surface of red blood cells. Type A has A antigens, Type B has B antigens, Type AB has both, and Type O has none.
-
The ABO blood group system is inherited from parents. Each person receives one allele from each parent, which can be A, B, or O.
Distribution of Blood Types
Blood types are not evenly distributed across the global population. Some types are more common in certain regions or ethnic groups.
-
Type O is the most common blood type worldwide. About 45% of people have Type O blood.
-
Type A is the second most common, with around 40% of the global population having this blood type.
-
Type B is less common, found in about 11% of people globally.
-
Type AB is the rarest, with only about 4% of the population having this blood type.
Compatibility and Transfusions
Blood transfusions require careful matching of blood types to prevent adverse reactions. Compatibility is crucial for safe medical procedures.
-
Type O negative is known as the universal donor. It can be given to patients of any blood type in emergencies.
-
Type AB positive is the universal recipient. People with this blood type can receive blood from any other type.
-
Mismatched blood transfusions can cause serious complications, including hemolytic reactions where the recipient's immune system attacks the donor blood cells.
Blood Type and Health
Your blood type can influence more than just transfusion compatibility. It may also affect your health in various ways.
-
People with Type O blood have a lower risk of heart disease compared to those with Type A, B, or AB.
-
Type A individuals may have a higher risk of stomach cancer and severe malaria.
-
Type B blood is associated with a higher risk of pancreatic cancer.
-
Type AB blood has been linked to an increased risk of cognitive impairment, including memory problems.
Blood Type and Personality
Some cultures believe that blood type can influence personality traits. This idea is especially popular in Japan and South Korea.
-
Type A individuals are often seen as calm, responsible, and patient.
-
Type B people are thought to be creative, passionate, and strong-willed.
-
Type AB individuals are considered rational, adaptable, and mysterious.
-
Type O people are often viewed as confident, self-determined, and outgoing.
Blood Type and Diet
The concept of blood type diets suggests that eating certain foods can improve health based on your blood type.
-
Type O individuals are advised to eat a high-protein diet, including lean meats and vegetables.
-
Type A people are recommended to follow a vegetarian diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
-
Type B individuals are encouraged to eat a balanced diet that includes dairy, meat, and vegetables.
-
Type AB people should focus on a mixed diet, combining elements from both Type A and Type B diets.
Fun and Unusual Facts
The ABO blood group system has some quirky and lesser-known aspects that might surprise you.
-
Mosquitoes are more attracted to people with Type O blood compared to other blood types.
-
Blood type can affect your susceptibility to certain infections. For example, people with Type O blood are less likely to contract norovirus.
-
Some animals, like cats and dogs, also have blood types, but their systems are different from humans.
-
Blood type can influence your body's response to stress. Type A individuals may produce more cortisol, the stress hormone.
-
In Japan, blood type is sometimes used in matchmaking and job applications, similar to how horoscopes are used in other cultures.
The Final Word on ABO Blood Groups
ABO blood groups are more than just letters on a medical chart. They play a crucial role in transfusions, organ transplants, and even disease susceptibility. Knowing your blood type can be a lifesaver in emergencies. It's fascinating how these four types—A, B, AB, and O—can tell so much about our health and genetic history. From the discovery by Karl Landsteiner to the modern-day implications, the ABO system remains a cornerstone of medical science. Whether you're donating blood or just curious about your genetic makeup, understanding these blood groups is essential. So next time you hear someone mention blood types, you'll know there's a lot more to it than meets the eye. Stay informed, stay healthy, and remember, your blood type is a vital part of who you are.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
