What is phytochrome? Phytochrome is a light-sensitive protein found in plants, algae, and some bacteria. It acts like a switch, helping plants sense light and adapt to their environment. This protein plays a crucial role in regulating growth, flowering, and seed germination. Imagine it as a plant's internal clock, telling it when to grow or bloom based on the light it receives. Understanding phytochrome can help scientists improve crop yields and develop plants that can thrive in different conditions. Ready to dive into some fascinating facts about this incredible protein? Let's get started!
What is Phytochrome?
Phytochrome is a type of photoreceptor in plants, bacteria, and fungi. It plays a crucial role in regulating various aspects of growth and development. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about this essential molecule.
-
Phytochromes are sensitive to light, particularly red and far-red wavelengths. This sensitivity allows plants to detect light conditions and adjust their growth accordingly.
-
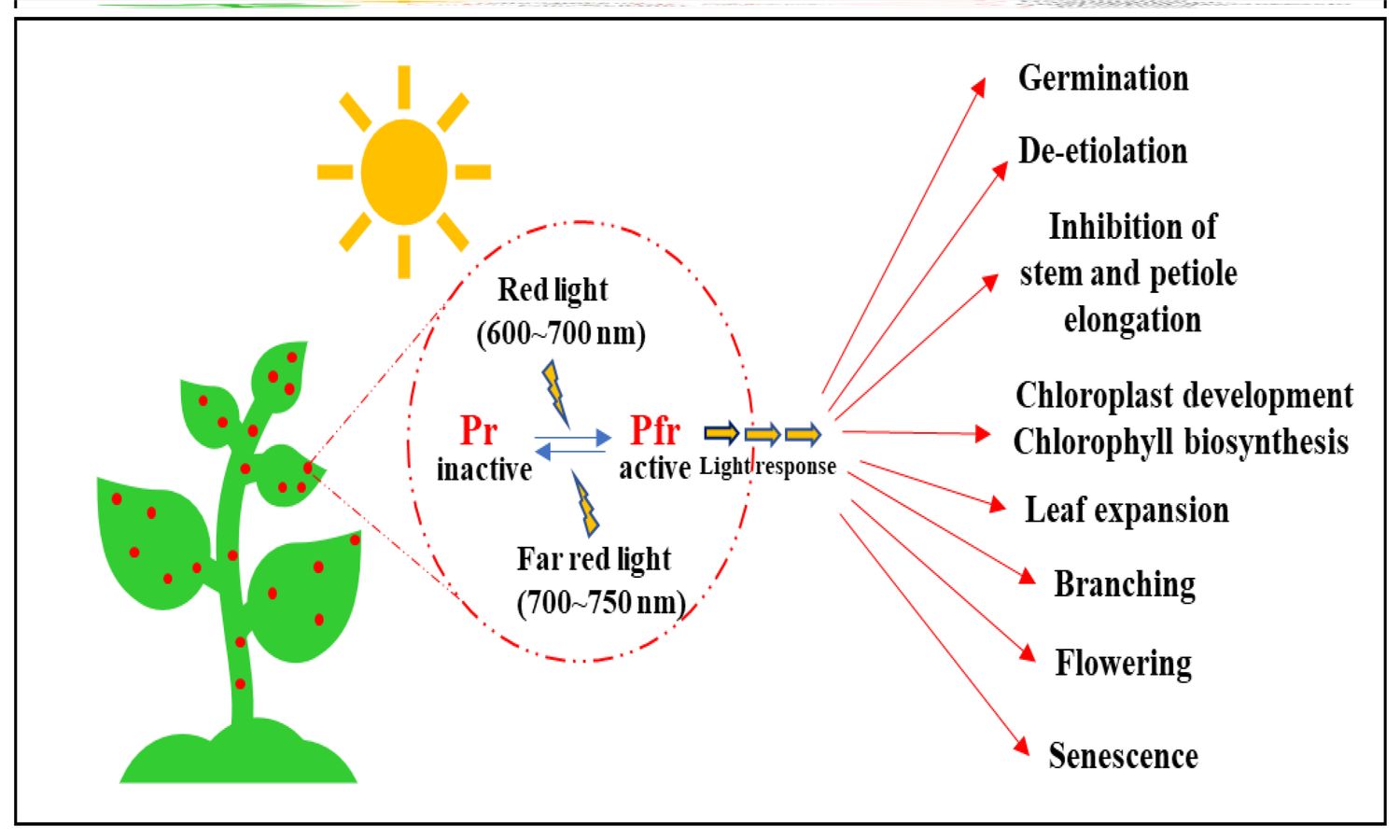
These photoreceptors exist in two forms: Pr and Pfr. Pr absorbs red light, while Pfr absorbs far-red light. The conversion between these forms helps plants respond to changing light environments.
-
Phytochrome was first discovered in the 1950s by American botanist Sterling B. Hendricks and his colleagues. Their research laid the foundation for understanding how light influences plant growth.
How Phytochrome Affects Plant Growth
Phytochrome's ability to sense light conditions directly impacts how plants grow and develop. Here are some ways it influences plant behavior.
-
Phytochrome regulates seed germination. Seeds exposed to red light via phytochrome are more likely to germinate, while far-red light inhibits this process.
-
It controls stem elongation. In low light conditions, phytochrome triggers plants to elongate their stems to reach more light.
-
Leaf expansion is also influenced by phytochrome. Adequate light conditions detected by phytochrome promote broader leaf growth for better photosynthesis.
-
Phytochrome helps plants detect shading from other plants. When shaded, plants can adjust their growth to compete for light.
Phytochrome and Flowering
Flowering is a critical stage in a plant's life cycle, and phytochrome plays a significant role in this process.
-
Phytochrome helps regulate the timing of flowering. It ensures that plants flower at the optimal time for pollination and seed production.
-
In long-day plants, phytochrome promotes flowering when days are long. Conversely, in short-day plants, it inhibits flowering during long days.
-
Phytochrome interacts with other hormones like gibberellins to control flowering. This interaction ensures a coordinated response to environmental signals.
Phytochrome in Agriculture
Understanding phytochrome can have practical applications in agriculture, helping improve crop yields and quality.
-
Manipulating light conditions in greenhouses can optimize phytochrome activity, leading to better crop growth.
-
Phytochrome research has led to the development of crops that can grow in varying light conditions, increasing agricultural productivity.
-
Scientists are exploring ways to engineer phytochrome pathways to create crops that are more resilient to climate change.
Phytochrome in Other Organisms
While phytochrome is best known for its role in plants, it also exists in other organisms.
-
Some bacteria possess phytochrome-like proteins that help them respond to light. This ability can influence their behavior and survival.
-
Fungi also have phytochrome proteins. These proteins help fungi adapt to their light environment, affecting their growth and reproduction.
Interesting Phytochrome Facts
Phytochrome is a complex and fascinating molecule with many intriguing aspects.
-
Phytochrome can exist in a stable form for extended periods, allowing plants to "remember" past light conditions.
-
The structure of phytochrome includes a light-absorbing chromophore, which is essential for its function.
-
Phytochrome research has revealed that light can influence gene expression in plants. This discovery has broad implications for understanding plant biology.
-
Some plants have multiple types of phytochrome, each with specific roles. This diversity allows for fine-tuned responses to light.
-
Phytochrome can interact with other photoreceptors, such as cryptochromes and phototropins, to coordinate plant responses to light.
-
The study of phytochrome has led to advances in biotechnology, including the development of light-controlled gene expression systems.
-
Phytochrome research has applications beyond agriculture, including in medicine and environmental science.
-
Scientists are investigating how phytochrome pathways can be harnessed to create sustainable energy solutions.
-
The discovery of phytochrome has inspired new technologies, such as light-sensitive materials and sensors.
-
Phytochrome continues to be a vibrant area of research, with ongoing studies uncovering new functions and mechanisms.
-
Understanding phytochrome can help address global challenges, such as food security and climate change, by improving plant resilience and productivity.
Final Thoughts on Phytochrome
Phytochrome is a fascinating plant pigment that plays a crucial role in how plants grow and respond to light. This pigment helps plants detect light changes, allowing them to adapt to their environment. From seed germination to flowering, phytochrome influences many stages of a plant's life cycle. Understanding this pigment can lead to advancements in agriculture, such as improving crop yields and developing plants that can thrive in various light conditions.
Knowing these facts about phytochrome can deepen your appreciation for the complex world of plants. Whether you're a student, gardener, or just curious, this knowledge can be quite enlightening. So next time you see a plant turning towards the light, remember the tiny but mighty pigment working behind the scenes. Phytochrome may be small, but its impact on plant life is enormous.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
