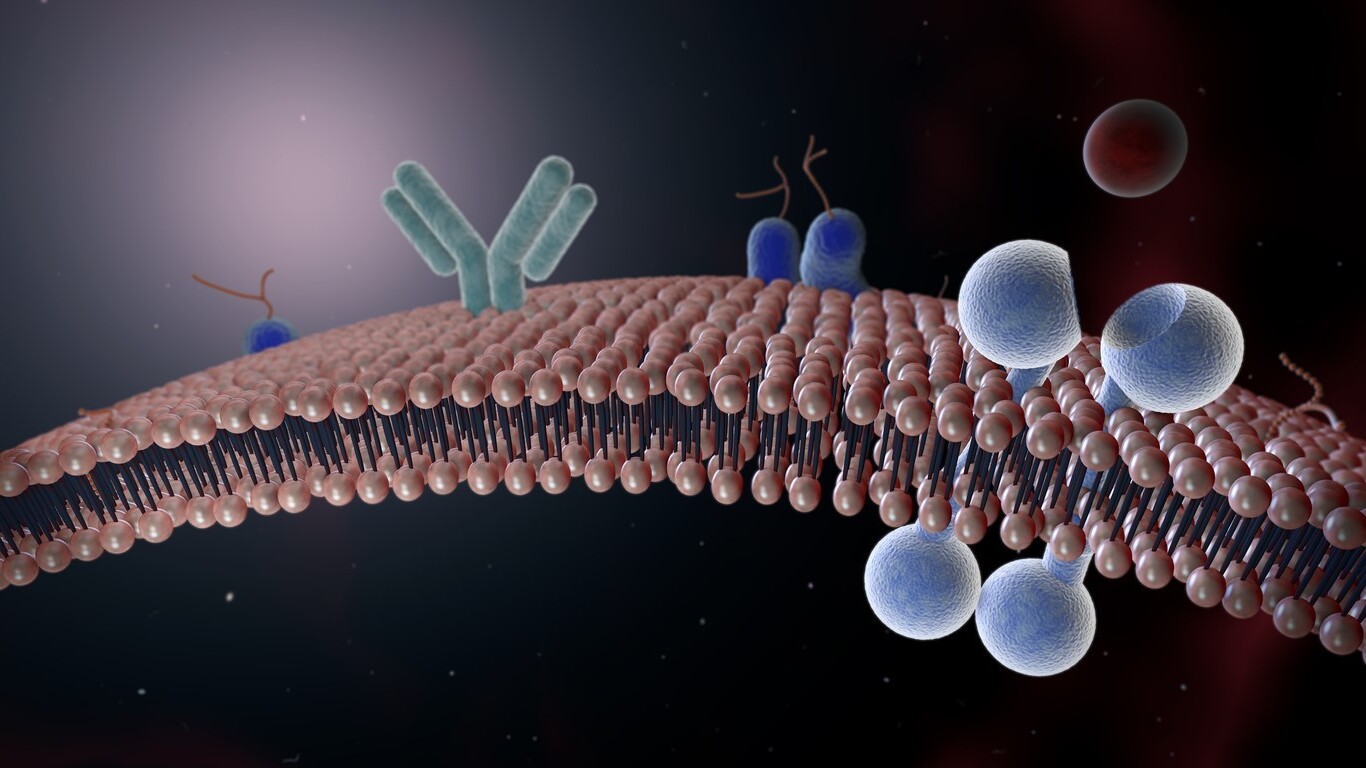
Membrane proteins are essential components of cells, playing critical roles in various biological processes. These proteins are embedded in or associated with the cell membrane, acting as gatekeepers, transporters, and communicators. Did you know that membrane proteins make up about 30% of all proteins in the human body? They are involved in vital functions such as signaling, transport, and maintaining cell structure. From helping nutrients enter cells to enabling communication between cells, these proteins are indispensable. Understanding membrane proteins can provide insights into how cells function and how diseases develop. Whether you're a student, a science enthusiast, or just curious, these 25 facts about membrane proteins will expand your knowledge and appreciation of these fascinating molecules.
What Are Membrane Proteins?
Membrane proteins are essential for various cellular functions. They reside within or on the surface of cell membranes, playing critical roles in communication, transport, and structural integrity.
- Integral Membrane Proteins: These proteins are embedded within the lipid bilayer, often spanning the entire membrane.
- Peripheral Membrane Proteins: These proteins attach to the membrane's surface, usually through interactions with integral proteins or lipid molecules.
- Lipid-Anchored Proteins: These proteins are covalently attached to lipids within the membrane, anchoring them in place.
Functions of Membrane Proteins
Membrane proteins perform a variety of tasks essential for cell survival and function. Here are some key roles they play:
- Transport: They help move substances across the cell membrane, including ions, nutrients, and waste products.
- Signal Transduction: These proteins act as receptors for signaling molecules, transmitting information into the cell.
- Cell Adhesion: Membrane proteins help cells stick to each other and to the extracellular matrix, maintaining tissue structure.
- Enzymatic Activity: Some membrane proteins function as enzymes, catalyzing chemical reactions at the membrane surface.
- Cell Recognition: They play a role in identifying and interacting with other cells, crucial for immune response and tissue formation.
Types of Membrane Proteins
Membrane proteins come in various forms, each with unique structures and functions. Here are some common types:
- Channel Proteins: These proteins form pores that allow specific ions or molecules to pass through the membrane.
- Carrier Proteins: They bind to specific substances and change shape to transport them across the membrane.
- Receptor Proteins: These proteins bind to signaling molecules, triggering a response inside the cell.
- Glycoproteins: Membrane proteins with carbohydrate groups attached, important for cell recognition and signaling.
- Aquaporins: Specialized channel proteins that facilitate water transport across the membrane.
Importance in Health and Disease
Membrane proteins are crucial for maintaining health and are often implicated in various diseases. Here are some facts highlighting their importance:
- Drug Targets: Many drugs target membrane proteins, making them essential for pharmaceutical development.
- Genetic Disorders: Mutations in membrane protein genes can lead to diseases such as cystic fibrosis and muscular dystrophy.
- Cancer: Abnormal membrane protein function can contribute to cancer progression and metastasis.
- Infectious Diseases: Pathogens often exploit membrane proteins to enter and infect host cells.
- Neurodegenerative Diseases: Dysfunctional membrane proteins are linked to conditions like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease.
Membrane Protein Structure
Understanding the structure of membrane proteins is key to grasping their function. Here are some insights into their structural characteristics:
- Alpha Helices: Many membrane proteins contain alpha-helical segments that span the lipid bilayer.
- Beta Barrels: Some proteins form beta-barrel structures, creating pores in the membrane.
- Hydrophobic Regions: Membrane-spanning regions are typically hydrophobic, allowing them to interact with the lipid bilayer.
- Extracellular and Intracellular Domains: Membrane proteins often have distinct regions that extend outside and inside the cell, each with specific functions.
Techniques for Studying Membrane Proteins
Studying membrane proteins presents unique challenges due to their complex nature. Here are some methods used by scientists:
- X-ray Crystallography: This technique helps determine the 3D structure of membrane proteins at atomic resolution.
- Cryo-Electron Microscopy: A powerful method for visualizing membrane proteins in their native environment.
- NMR Spectroscopy: Used to study the structure and dynamics of membrane proteins in solution.
Membrane Proteins: Essential and Fascinating
Membrane proteins are vital for life. They control what enters and exits cells, making them crucial for cell function. These proteins also play a key role in communication between cells, helping organisms respond to their environment. Understanding membrane proteins can lead to breakthroughs in medicine, such as new treatments for diseases like cancer and diabetes.
Research on these proteins is ongoing, with scientists constantly discovering new functions and mechanisms. This knowledge can improve drug design, making treatments more effective and targeted. Membrane proteins are not just important for health; they also have industrial applications, like in biotechnology and environmental science.
In short, membrane proteins are indispensable. Their study not only advances science but also holds the promise of better health and innovative technologies. Keep an eye on this field; it's full of potential and exciting discoveries.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
