Ever wondered what makes botfly larvae so intriguing? These tiny creatures have a life cycle that's both fascinating and a bit creepy. Found in various parts of the world, botflies are known for their unique way of reproducing. Female botflies lay eggs on mosquitoes or other insects, which then transfer the eggs to mammals, including humans. Once the eggs hatch, the larvae burrow into the host's skin, causing discomfort and sometimes infection. Despite their unsettling nature, botfly larvae play a crucial role in the ecosystem. They help control insect populations and serve as food for other animals. Ready to learn more? Here are 35 facts that will give you a deeper understanding of these remarkable insects.
Key Takeaways:
- Botfly larvae are parasitic insects that can infect a variety of hosts, including humans, and their presence can cause discomfort and health issues. Preventative measures and early detection are crucial for minimizing their impact.
- Botfly larvae play a role in the ecosystem by interacting with wildlife, and while they are parasitic, they contribute to the balance of ecosystems. Understanding their life cycle and impact is essential for wildlife conservation.
What Are Botfly Larvae?
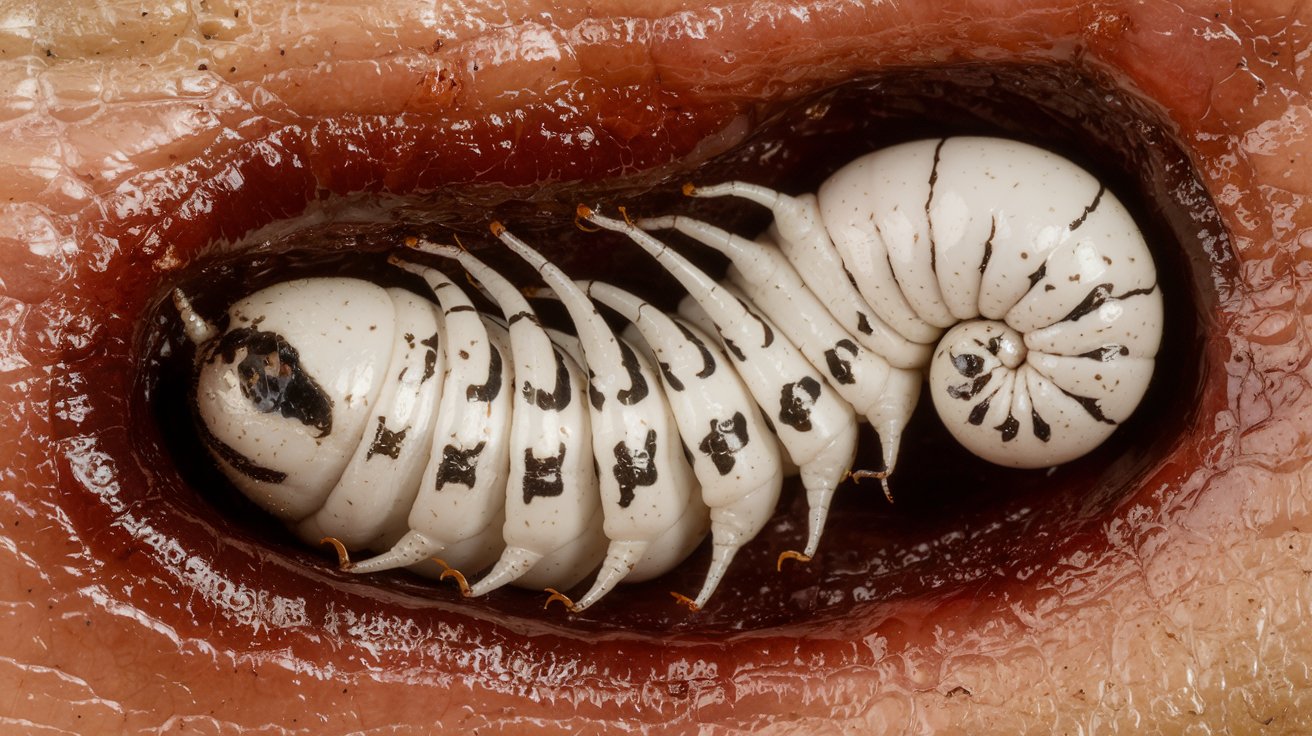
Botfly larvae are the immature stage of botflies, which are parasitic insects. These larvae are known for their unique and often unsettling life cycle. Here are some fascinating facts about them.
-
Botflies belong to the family Oestridae, which includes several species known for their parasitic larvae.
-
The adult botfly lays its eggs on a host, often using other insects like mosquitoes to transfer the eggs.
-
Once the eggs hatch, the larvae burrow into the host's skin, where they develop.
-
Botfly larvae can infect a variety of hosts, including humans, mammals, and birds.
-
The larvae create a small hole in the host's skin to breathe while they grow.
Life Cycle of Botfly Larvae
Understanding the life cycle of botfly larvae can be both fascinating and a bit creepy. Here are some key points about their development.
-
The life cycle begins when an adult female botfly lays her eggs on a host or an intermediate carrier.
-
The eggs hatch into larvae, which then penetrate the host's skin.
-
Inside the host, the larvae go through several stages of development, known as instars.
-
The entire development process can take several weeks to months, depending on the species and environmental conditions.
-
Once fully developed, the larvae exit the host's body to pupate in the soil.
Impact on Hosts
Botfly larvae can have various effects on their hosts, ranging from mild irritation to severe health issues. Here are some facts about their impact.
-
The presence of botfly larvae in the skin can cause intense itching and discomfort.
-
In some cases, the larvae can cause secondary bacterial infections if the wound is not kept clean.
-
The larvae secrete enzymes that break down tissue, which can lead to tissue damage.
-
Some hosts may develop allergic reactions to the larvae or their secretions.
-
In livestock, botfly infestations can lead to decreased productivity and economic losses.
Botfly Larvae in Humans
Botfly larvae can occasionally infect humans, leading to a condition known as myiasis. Here are some facts about human botfly infestations.
-
Human botfly infestations are most common in tropical and subtropical regions.
-
The most common species to infect humans is Dermatobia hominis, also known as the human botfly.
-
Symptoms of a botfly larva infection include a raised, red bump on the skin, often with a small hole in the center.
-
The larvae can be felt moving under the skin, which can be quite distressing.
-
Treatment usually involves removing the larvae, either through surgical extraction or suffocation techniques.
Prevention and Treatment
Preventing and treating botfly larvae infestations can be challenging but is essential for minimizing their impact. Here are some key points.
-
Using insect repellent can help reduce the risk of being bitten by insects that carry botfly eggs.
-
Wearing protective clothing can also help prevent exposure to botfly larvae.
-
Regularly checking pets and livestock for signs of botfly larvae can help catch infestations early.
-
In some cases, applying petroleum jelly or adhesive tape over the breathing hole can suffocate the larvae, forcing them to come out.
-
Surgical removal by a healthcare professional is often the most effective way to treat a botfly larva infection.
Interesting Facts
Botfly larvae have some unique and intriguing characteristics. Here are some lesser-known facts about them.
-
Botfly larvae have specialized mouthparts that allow them to anchor themselves firmly in the host's tissue.
-
The larvae can secrete antimicrobial substances to prevent infection in the host.
-
Some species of botflies have evolved to target specific hosts, such as rodents or deer.
-
The adult botfly does not feed; its sole purpose is to reproduce and lay eggs.
-
Botfly larvae have been used in scientific research to study host-parasite interactions.
Botfly Larvae and Wildlife
Botfly larvae also play a role in the ecosystem, particularly in their interactions with wildlife. Here are some facts about their relationship with wild animals.
-
Many species of wild mammals, such as rabbits and squirrels, are common hosts for botfly larvae.
-
In some ecosystems, botfly larvae infestations can help control the population of certain animal species.
-
Birds can also be hosts for botfly larvae, which can affect their health and reproductive success.
-
Some predators, like certain species of birds, have learned to recognize and remove botfly larvae from their prey.
-
Despite their parasitic nature, botfly larvae contribute to the biodiversity and balance of ecosystems.
Final Thoughts on Botfly Larvae
Botfly larvae are fascinating yet unsettling creatures. These parasites, known for burrowing into the skin of mammals, including humans, have a unique life cycle that involves using a host to develop. While the idea of having a botfly larva under your skin might sound like a scene from a horror movie, it's a natural part of their existence. Understanding these creatures helps demystify their role in the ecosystem and highlights the intricate balance of nature. If you ever find yourself in a region where botflies are common, taking preventive measures can save you from an uncomfortable encounter. Remember, knowledge is power. The more you know about these tiny invaders, the better prepared you'll be to avoid them. Stay curious, stay informed, and always respect the wonders of the natural world, no matter how creepy they might seem.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


