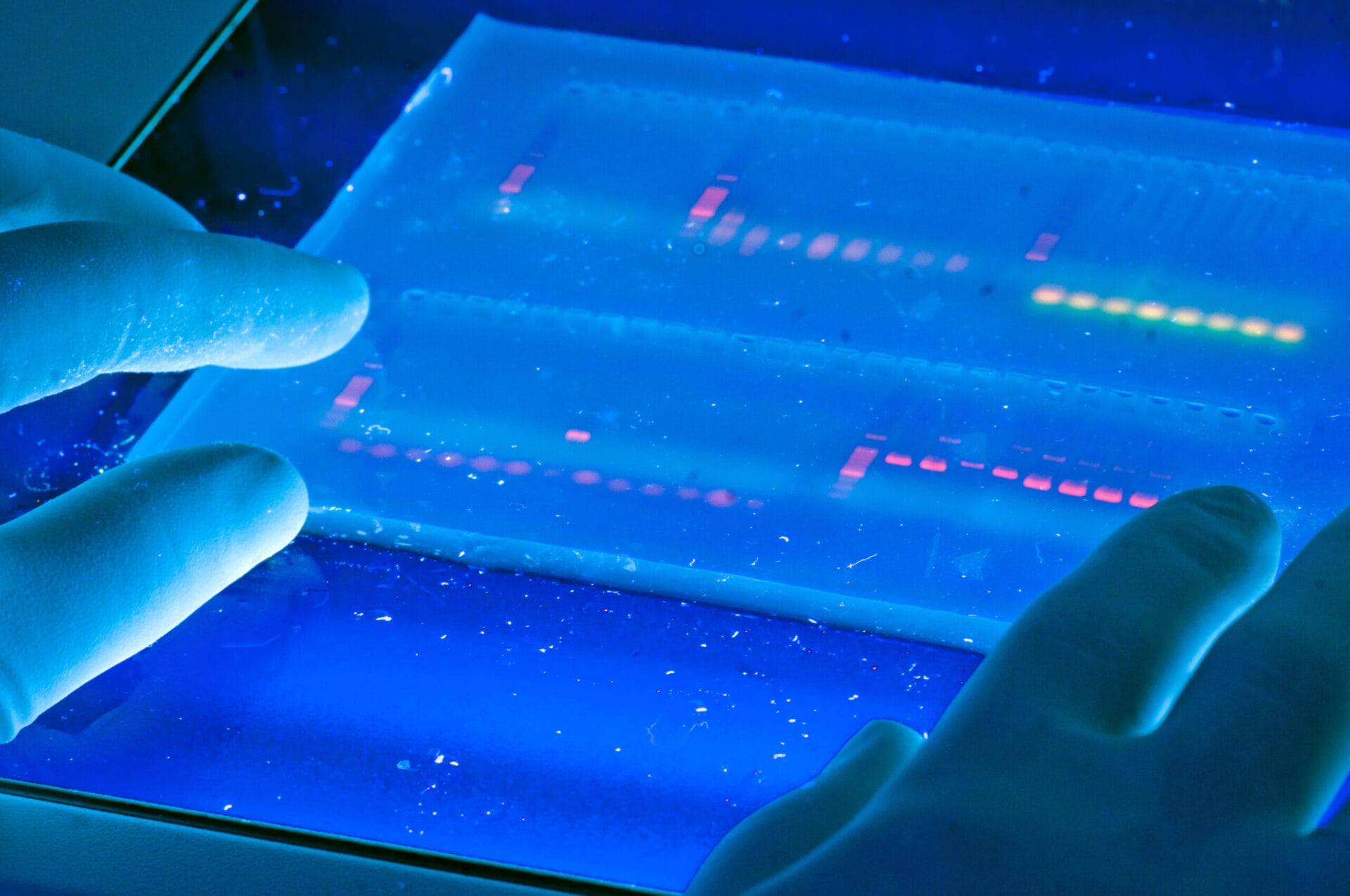
What is gel electrophoresis? It's a technique used to separate DNA, RNA, or proteins based on size and charge. Imagine a jelly-like substance where molecules move when an electric current passes through. Smaller fragments travel faster, while larger ones lag behind. This method helps scientists analyze genetic material, identify proteins, and even solve crimes. Why is it important? Gel electrophoresis plays a crucial role in research, medicine, and forensic science. It allows for the examination of genetic disorders, the development of new treatments, and the identification of individuals in criminal cases. Understanding this process can open doors to fascinating discoveries in biology and beyond.
What is Gel Electrophoresis?
Gel electrophoresis is a technique used to separate DNA, RNA, or proteins based on their size and charge. This method is widely used in molecular biology, genetics, and biochemistry labs. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about this essential scientific tool.
-
Invented in the 1950s: Gel electrophoresis was first developed in the 1950s by scientists Oliver Smithies and Arne Tiselius.
-
Uses an Electric Field: The process involves applying an electric field to a gel matrix, causing molecules to migrate through the gel.
-
Agarose and Polyacrylamide Gels: Two main types of gels are used: agarose for DNA and RNA, and polyacrylamide for proteins.
-
Molecular Sieving: The gel acts like a sieve, allowing smaller molecules to move faster than larger ones.
-
Visualizing Results: After separation, molecules are often stained with dyes like ethidium bromide to visualize the bands under UV light.
How Does Gel Electrophoresis Work?
Understanding the mechanics behind gel electrophoresis can help appreciate its utility in scientific research. Here's a closer look at how it operates.
-
Sample Loading: Samples are loaded into wells at one end of the gel.
-
Buffer Solution: The gel is submerged in a buffer solution that conducts electricity.
-
Electric Current: An electric current is applied, causing negatively charged molecules to move towards the positive electrode.
-
Migration Rate: The rate of migration depends on the molecule's size and charge.
-
Band Formation: Molecules form distinct bands as they separate, which can be analyzed for various purposes.
Applications of Gel Electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis is not just a lab technique; it has numerous applications in different fields. Here are some of its key uses.
-
DNA Fingerprinting: Used in forensic science to identify individuals based on their DNA profiles.
-
Genetic Research: Helps in studying genetic variations and mutations.
-
Protein Analysis: Essential for analyzing protein mixtures in biochemistry.
-
RNA Studies: Used to study RNA molecules and their functions.
-
PCR Product Analysis: Commonly used to check the results of PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) experiments.
Advantages of Gel Electrophoresis
Why is gel electrophoresis so popular among scientists? Here are some of its advantages.
-
High Resolution: Provides high-resolution separation of molecules.
-
Versatility: Can be used for DNA, RNA, and proteins.
-
Cost-Effective: Relatively inexpensive compared to other separation techniques.
-
Ease of Use: Simple to set up and perform.
-
Quantitative Analysis: Allows for quantitative analysis of molecular samples.
Limitations of Gel Electrophoresis
Despite its many advantages, gel electrophoresis has some limitations. Let's explore these drawbacks.
-
Time-Consuming: The process can be time-consuming, especially for large samples.
-
Limited Sample Size: Only small amounts of sample can be loaded into the gel.
-
Resolution Limits: Limited resolution for very large or very small molecules.
-
Staining Issues: Staining and destaining steps can be tricky and may affect results.
-
Equipment Costs: Initial setup costs for equipment can be high.
Innovations in Gel Electrophoresis
Science never stands still, and neither does gel electrophoresis. Here are some recent innovations in this field.
-
Capillary Electrophoresis: Uses capillaries instead of gels for faster and more efficient separation.
-
Microfluidic Devices: Miniaturized systems that offer high-throughput analysis.
-
Automated Systems: Automation has made the process faster and more reliable.
-
Real-Time Analysis: New techniques allow for real-time monitoring of the separation process.
-
Improved Stains: Development of safer and more effective staining methods.
Fun Facts About Gel Electrophoresis
Let's end with some fun and lesser-known facts about gel electrophoresis.
-
DNA Art: Scientists have used gel electrophoresis to create artistic patterns with DNA.
-
Educational Tool: Often used in educational settings to teach students about molecular biology.
-
Historical Impact: Played a crucial role in the Human Genome Project.
-
Pop Culture: Featured in TV shows and movies that involve forensic science.
Final Thoughts on Gel Electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis is a powerful tool in molecular biology. It separates DNA, RNA, and proteins based on size and charge, making it essential for genetic research, forensic science, and medical diagnostics. Understanding the basics, like how the gel matrix works and the role of the electric field, helps grasp its importance.
This technique has revolutionized how scientists study genetic material. From identifying genetic disorders to solving crimes, gel electrophoresis has countless applications. It’s fascinating how a simple process can provide so much information.
Whether you're a student, a researcher, or just curious, knowing these facts about gel electrophoresis can deepen your appreciation for this scientific method. It’s a testament to human ingenuity and the quest for knowledge. Keep exploring, stay curious, and who knows what other amazing discoveries await in the world of science.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


