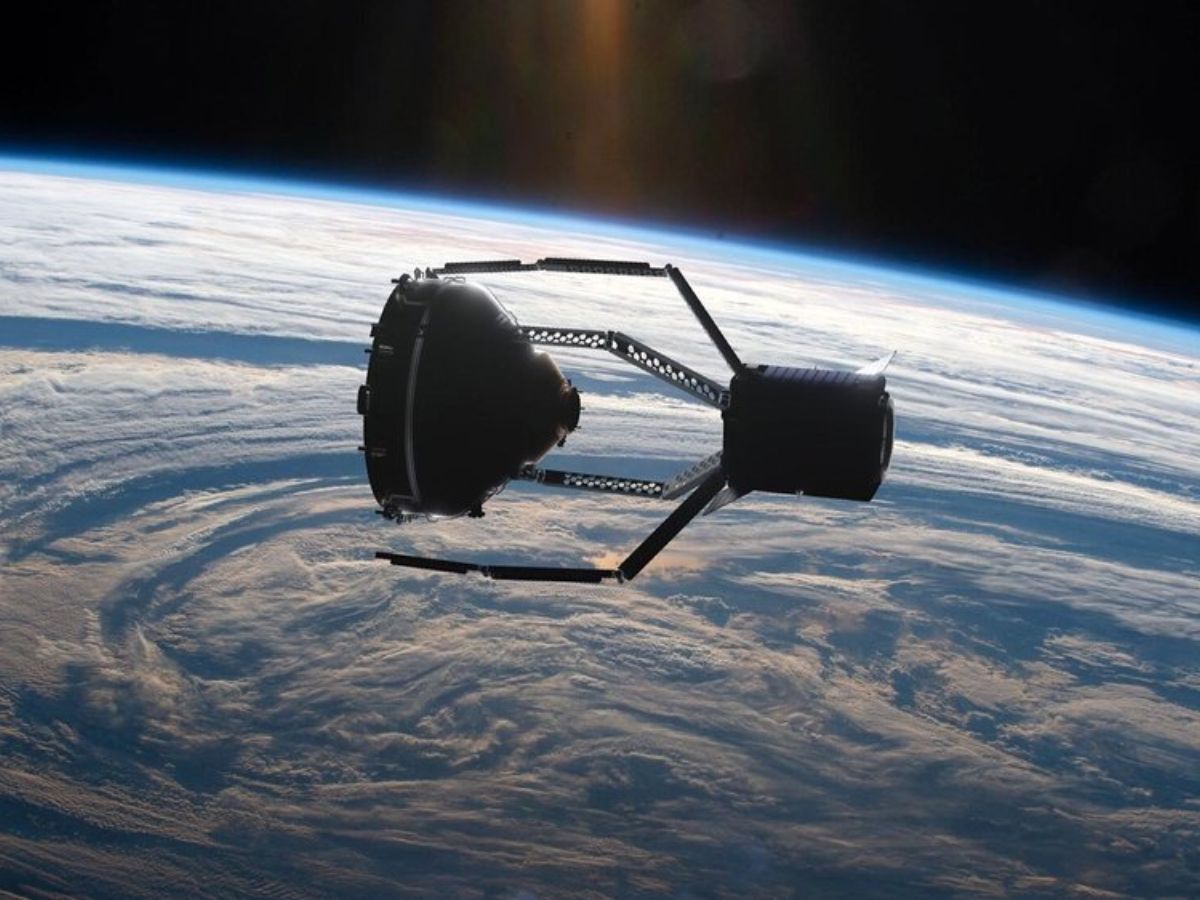
Space, vast and mysterious, is home to not just celestial bodies but also to a growing concern: space debris. Active debris removal (ADR) has emerged as a critical solution to this issue, aiming to clean up the clutter orbiting our planet. From defunct satellites to spent rocket stages, the junk floating in space poses a significant risk to operational satellites and human spaceflight. In this blog post, we'll unveil 15 intriguing facts about ADR, shedding light on how scientists and engineers are tackling the challenge of space junk. Whether you're a space enthusiast or simply curious about the efforts to preserve the cosmos for future generations, these facts will provide a comprehensive overview of the innovative methods and technologies being developed to keep our orbits clean and safe.
Understanding Active Debris Removal
Space debris, also known as space junk, includes defunct satellites, spent rocket stages, and fragments from disintegration, erosion, and collisions. As orbit around Earth becomes increasingly crowded, active debris removal (ADR) has emerged as a crucial method to mitigate collision risks and ensure the long-term sustainability of space activities.
-
Active Debris Removal (ADR) refers to various methods and technologies developed to remove non-functional satellites and debris from orbit. This process is vital for preventing potential collisions that could generate more debris, leading to the Kessler Syndrome—a scenario where the density of objects in low Earth orbit is high enough to cause collisions between objects, creating a cascading effect of increasingly more debris.
-
The concept of ADR is not just theoretical; several missions and technologies are in development or have been tested. For instance, the RemoveDEBRIS mission, launched in 2018, successfully demonstrated the use of a net and a harpoon to capture and deorbit space debris.
The Technologies Behind ADR
-
Robotic arms are among the technologies proposed for ADR. These arms could be used to grab larger pieces of debris and either move them to a safer orbit or direct them towards Earth's atmosphere, where they would burn up harmlessly.
-
Lasers have also been suggested as a means to either push debris into lower orbits, where atmospheric drag would expedite their re-entry, or to directly ablate them, reducing their size and mass.
-
Harpoons and nets are not just concepts but have been actively tested in space. These methods aim to capture debris so it can be moved or deorbited, demonstrating a practical approach to cleaning up space.
The Challenges of ADR
-
One major challenge is the cost. Designing, launching, and operating ADR missions require significant financial investment, making it difficult to justify and fund these initiatives.
-
Legal and political hurdles also pose significant challenges. Space is governed by international law, which currently lacks clear regulations regarding debris removal. Determining who is responsible for which pieces of debris and who has the authority to remove them complicates efforts to clean up space.
-
Technical difficulties in accurately tracking and capturing small or spinning debris add another layer of complexity to ADR missions. The vastness of space and the high velocities involved make these operations extremely challenging.
The Importance of International Collaboration
-
Global cooperation is essential for the success of ADR efforts. Space debris is a problem that affects all nations with satellites in orbit, and collaborative approaches are necessary to develop, fund, and implement effective removal strategies.
-
Joint missions between countries and organizations can pool resources and expertise, making ADR more feasible and cost-effective. For example, the European Space Agency (ESA) has been actively working on the e.Deorbit mission, which aims to demonstrate ADR capabilities by targeting and removing a large piece of debris from orbit.
Future Prospects of ADR
-
Looking ahead, new technologies such as magnetic tethers and ion beams are being explored as potential methods for debris removal. These innovative solutions could offer more efficient and less costly ways to clean up space.
-
Commercial ADR services are also emerging as space becomes more congested. Companies are beginning to see the potential for profit in debris removal, which could lead to increased investment and innovation in the field.
-
Regulatory frameworks are evolving to support ADR initiatives. As the international community recognizes the importance of maintaining a clean and safe orbital environment, laws and policies are being developed to facilitate debris removal.
-
Public awareness of the space debris problem and the need for ADR is growing. This increased attention could drive political and financial support for ADR missions, highlighting the role of public opinion in shaping space policy.
-
Finally, educational programs and initiatives aimed at raising awareness about space sustainability are crucial. By educating the next generation of scientists, engineers, and policymakers about the importance of ADR, we can ensure continued progress in making space safer for all.
A Final Glimpse at Space Clean-Up
Active debris removal isn't just a futuristic concept; it's a crucial step toward safeguarding our orbital environment for generations to come. With over 27,000 pieces of space junk whizzing around Earth, the risk of collisions and the potential for a cascading effect, known as the Kessler Syndrome, is real. Initiatives by various organizations and governments highlight the urgency and importance of addressing space debris. Technologies like nets, harpoons, and lasers are not scenes from a sci-fi movie but real solutions being tested and deployed to tackle this challenge. As we push the boundaries of space exploration, ensuring the sustainability of outer space is a responsibility we all share. Let's keep our eyes on the stars, but also on preserving the vast expanse that makes reaching them possible.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.