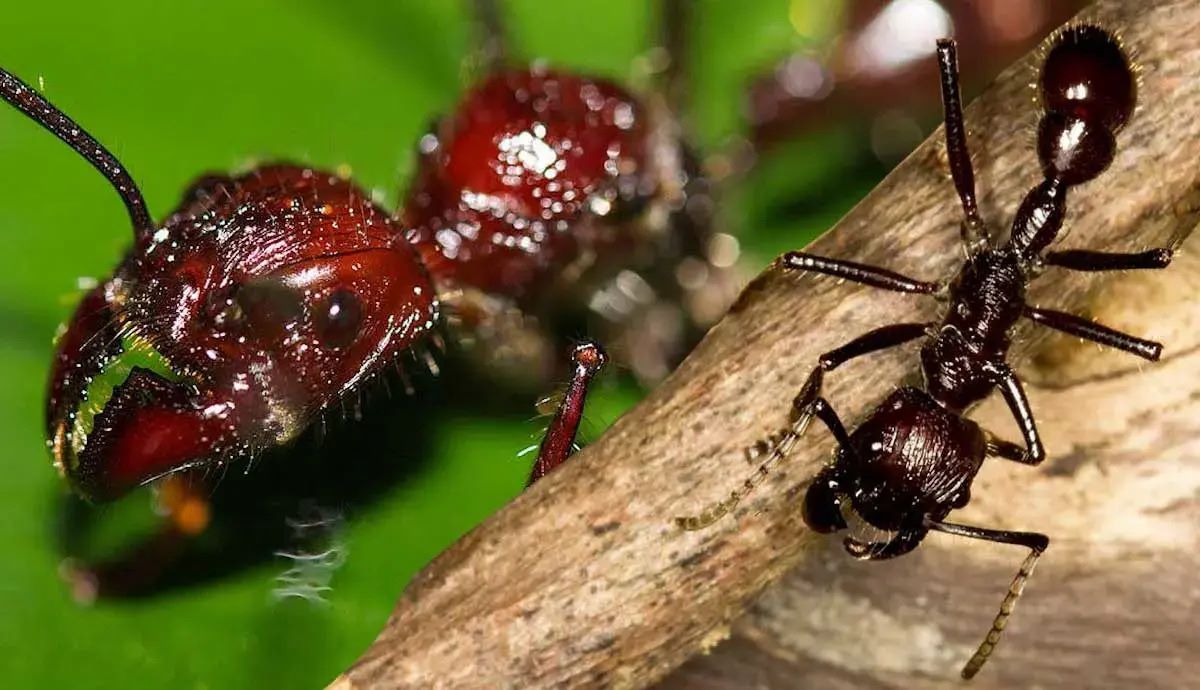
Ever wondered what it's like to be stung by a bullet ant? Known for having one of the most painful stings in the insect world, these tiny warriors pack a punch. Found mainly in the rainforests of Central and South America, bullet ants are fascinating creatures with unique behaviors and characteristics. Their sting is often compared to being shot, hence the name. But there's more to these ants than just their painful bite. From their complex social structures to their role in indigenous rituals, bullet ants are a marvel of nature. Ready to learn some mind-blowing facts about these incredible insects? Buckle up, because you're in for a wild ride!
Key Takeaways:
- Bullet ants are giant, black ants with a sting that feels like being shot by a bullet. Their painful sting is used for defense and has cultural significance in some Amazonian tribes.
- Bullet ants have a complex social structure, communicate through pheromones, and are important for scientific research. Efforts are being made to raise public awareness about their ecological importance.
Bullet Ants: Nature's Tiny Warriors
Bullet ants, known for their excruciating sting, are fascinating creatures. These ants, native to Central and South America, have unique traits that make them stand out in the insect world. Let's dive into some intriguing facts about these tiny warriors.
-
Scientific Name: The bullet ant's scientific name is Paraponera clavata. This name reflects its classification in the ant family.
-
Common Name Origin: They are called bullet ants because their sting feels like being shot by a bullet.
-
Pain Scale: Their sting ranks at the top of the Schmidt Sting Pain Index, a scale that measures the pain of insect stings.
-
Habitat: Bullet ants are typically found in humid rainforests from Nicaragua to Paraguay.
-
Size: These ants are among the largest in the world, measuring up to 1.2 inches in length.
-
Color: Bullet ants are usually black or dark brown, which helps them blend into their forest environment.
-
Diet: They primarily feed on nectar and small insects.
-
Predators: Despite their painful sting, bullet ants have predators like birds and larger insects.
-
Colony Structure: A bullet ant colony can have several hundred members, including workers, males, and a queen.
-
Lifespan: Worker ants live for several months, while queens can live for years.
The Sting: A Painful Encounter
The bullet ant's sting is infamous for its intensity. Here are some facts about this painful encounter.
-
Duration of Pain: The pain from a bullet ant sting can last up to 24 hours.
-
Description of Pain: Victims describe the pain as intense, throbbing, and burning.
-
Purpose of Sting: The sting is primarily used for defense against predators and threats to the colony.
-
Venom Composition: The venom contains poneratoxin, a neurotoxic peptide that affects the nervous system.
-
Allergic Reactions: Some people may experience severe allergic reactions to the sting, requiring medical attention.
-
Traditional Use: In some indigenous cultures, bullet ant stings are used in initiation rites to test endurance and bravery.
-
Sting Frequency: Unlike bees, bullet ants can sting multiple times without dying.
-
Warning Signs: Before stinging, bullet ants often raise their front legs as a warning.
-
Pain Management: Applying ice and taking pain relievers can help manage the pain from a sting.
-
Sting Location: The sting is most painful when delivered to sensitive areas like fingers or toes.
Social Structure and Behavior
Bullet ants have a complex social structure and exhibit fascinating behaviors. Here are some insights into their social life.
-
Queen's Role: The queen's primary role is to lay eggs and ensure the colony's survival.
-
Worker Ants: Workers are responsible for foraging, defending the colony, and caring for the young.
-
Communication: Bullet ants communicate through pheromones, which help them coordinate activities and alert others to danger.
-
Nest Building: They build nests at the base of trees, using soil and plant material.
-
Territorial Behavior: Bullet ants are highly territorial and will aggressively defend their nest from intruders.
-
Foraging Habits: Foraging is usually done at night to avoid predators and the heat of the day.
-
Ant Trails: They create chemical trails to guide other ants to food sources.
-
Grooming: Ants groom each other to maintain hygiene and remove parasites.
-
Brood Care: Workers take turns caring for the eggs, larvae, and pupae, ensuring they develop properly.
-
Colony Relocation: If a nest becomes unsuitable, the colony can relocate to a new site.
Interaction with Humans
Bullet ants have a unique relationship with humans, especially in regions where they are native.
-
Cultural Significance: In some Amazonian tribes, bullet ants play a role in coming-of-age ceremonies.
-
Tourist Attraction: Their painful sting has made them a subject of interest for adventurous tourists.
-
Scientific Research: Scientists study bullet ants to understand pain mechanisms and develop new painkillers.
-
Conservation Status: While not endangered, habitat destruction poses a threat to their populations.
-
Educational Programs: Some educational programs use bullet ants to teach about biodiversity and rainforest ecosystems.
-
Ant Farms: Bullet ants are sometimes kept in ant farms for educational purposes, though their care requires expertise.
-
Documentaries: They have been featured in numerous documentaries highlighting their unique behaviors and painful sting.
-
Local Myths: Various myths and legends surround bullet ants in indigenous cultures, often emphasizing their strength and pain-inducing sting.
-
Medical Studies: Research on bullet ant venom has potential applications in medicine, particularly in pain management.
-
Public Awareness: Efforts are being made to raise public awareness about the ecological importance of bullet ants and the need to protect their habitats.
The Final Sting
Bullet ants are fascinating creatures with their powerful sting and unique behaviors. Known for their intense pain, these ants have earned a reputation that few other insects can match. Their sting, often compared to being shot, is a defense mechanism that protects their colonies from predators.
Living in the rainforests of Central and South America, bullet ants play a crucial role in their ecosystems. They help control pest populations and contribute to the health of their habitats. Despite their fearsome sting, they are not aggressive unless provoked.
Understanding these ants gives us a glimpse into the complexity of nature. Their social structures, survival strategies, and interactions with other species highlight the intricate balance within ecosystems. Next time you hear about bullet ants, remember their importance goes beyond their painful sting. They are a vital part of the natural world, deserving respect and admiration.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.