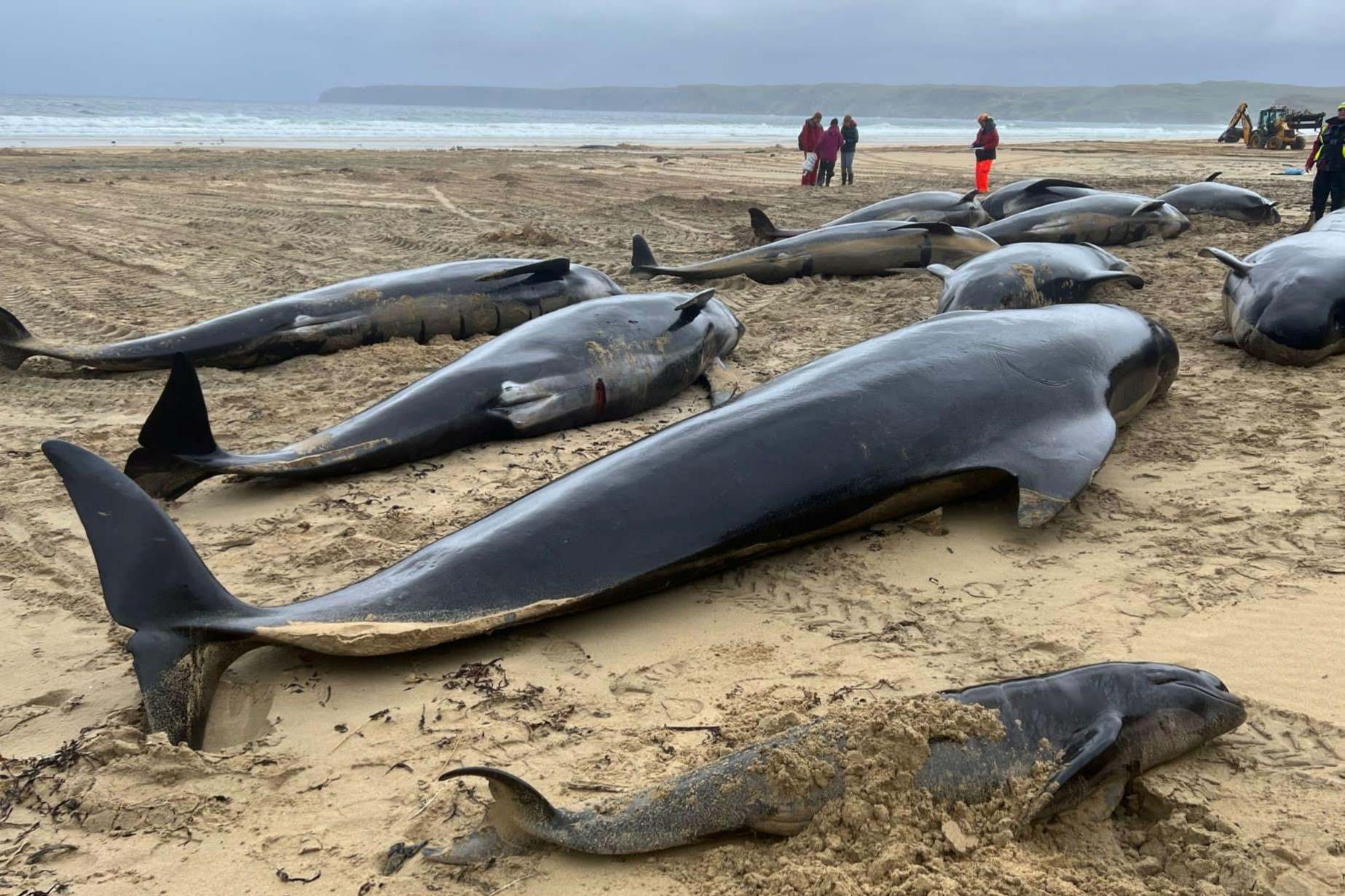
Why do pilot whales strand themselves on the shores of Scotland? This question has puzzled scientists and locals alike for years. Pilot whale strandings are tragic events where these intelligent marine mammals end up beached, often in large numbers. Scotland, with its rugged coastline, has seen its fair share of these incidents. Various theories exist, ranging from navigational errors to social bonding behaviors. Some believe that underwater noise pollution or changes in the Earth's magnetic field might play a role. Others think that a sick or injured leader could lead the entire pod astray. Understanding these strandings is crucial for developing strategies to prevent them and protect these magnificent creatures.
Key Takeaways:
- Pilot whales are social and intelligent marine mammals that often strand in Scotland due to navigation errors, illness, and human activity. Strandings have both positive and negative impacts on the local ecosystem.
- To help prevent pilot whale strandings, individuals can report sightings, volunteer for rescue efforts, reduce noise pollution, support conservation organizations, and stay informed about marine life conservation.
Pilot Whale Stranding in Scotland: A Closer Look
Pilot whale strandings are tragic events that capture the attention of marine biologists and the public alike. Scotland, with its extensive coastline, has witnessed several such incidents. Here are some fascinating facts about these occurrences.
What is a Pilot Whale?
Pilot whales are intriguing marine mammals known for their social behavior and intelligence. They often travel in large pods, making strandings particularly devastating.
- Species: Pilot whales belong to the dolphin family and are divided into two species: long-finned and short-finned.
- Size: These whales can grow up to 20 feet long and weigh as much as 3 tons.
- Diet: Their diet mainly consists of squid, but they also eat fish.
- Lifespan: They can live up to 60 years in the wild.
- Social Structure: Pilot whales are highly social and often travel in pods of 20-100 individuals.
Historical Strandings in Scotland
Scotland's coastline has been a hotspot for pilot whale strandings over the years. These events have provided valuable insights into the behavior and health of these marine mammals.
- First Recorded Stranding: The first recorded pilot whale stranding in Scotland dates back to the 18th century.
- Largest Stranding: In 2011, over 60 pilot whales stranded on the shores of the Outer Hebrides.
- Frequent Locations: The Western Isles and the Orkney Islands are common sites for these strandings.
- Seasonal Patterns: Most strandings occur during the summer months.
- Rescue Efforts: Local communities and marine biologists often collaborate to rescue stranded whales.
Causes of Stranding
Understanding why pilot whales strand themselves is crucial for preventing future incidents. Several factors contribute to these tragic events.
- Navigation Errors: Pilot whales use echolocation to navigate, and errors can lead them into shallow waters.
- Illness: Sick or injured whales may strand themselves.
- Social Bonds: Strong social bonds can cause entire pods to strand if one whale is in distress.
- Environmental Factors: Changes in water temperature and currents can disorient whales.
- Human Activity: Noise pollution from ships and underwater construction can interfere with their navigation.
Impact on Local Ecosystems
Strandings have significant effects on local ecosystems, both positive and negative. These events can alter the natural balance in various ways.
- Nutrient Input: Decomposing whale carcasses provide nutrients for marine and terrestrial ecosystems.
- Predator Attraction: Strandings can attract predators like sharks and scavengers such as birds.
- Habitat Disruption: Large carcasses can disrupt local habitats and marine life.
- Human Impact: Strandings often draw crowds, which can further disturb the local environment.
- Scientific Research: Strandings offer opportunities for scientific research, providing insights into whale health and behavior.
Conservation Efforts
Efforts to protect pilot whales and prevent strandings are ongoing. Various organizations and initiatives are dedicated to this cause.
- Marine Protected Areas: Establishing protected areas helps safeguard whale habitats.
- Rescue Training: Training programs for rescuers improve response times and success rates.
- Public Awareness: Educating the public about the importance of marine conservation.
- Research Funding: Increased funding for research on whale behavior and health.
- Policy Changes: Implementing policies to reduce noise pollution and other human impacts.
Notable Stranding Events
Several notable stranding events have occurred in Scotland, each with its unique circumstances and outcomes.
- 1992 Stranding: A pod of 30 pilot whales stranded near Durness, sparking a large rescue effort.
- 2008 Event: Over 50 whales stranded on the shores of Fife, with many successfully returned to the sea.
- 2012 Incident: A mass stranding in the Western Isles led to significant media coverage and public interest.
- 2015 Stranding: A smaller event in the Orkney Islands highlighted the ongoing issue of whale strandings.
- 2020 Stranding: The most recent significant stranding involved 20 whales near the Isle of Skye.
How You Can Help
Individuals can play a role in preventing strandings and aiding rescue efforts. Here are some ways to get involved.
- Report Strandings: If you see a stranded whale, report it to local authorities immediately.
- Volunteer: Join local marine conservation groups to assist in rescue efforts.
- Reduce Noise Pollution: Limit activities that contribute to underwater noise pollution.
- Support Conservation: Donate to organizations dedicated to marine conservation.
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with the latest research and news on marine life conservation.
Final Thoughts on Pilot Whale Stranding in Scotland
Pilot whale strandings in Scotland are a stark reminder of the fragile balance in marine ecosystems. These events often leave scientists puzzled, as the exact causes remain elusive. Factors like navigation errors, disease, and environmental changes are all potential culprits.
Understanding these strandings is crucial for conservation efforts. Each incident provides valuable data, helping researchers develop strategies to prevent future occurrences. Community involvement also plays a significant role. Local volunteers often assist in rescue operations, showcasing the power of collective action.
Raising awareness about these strandings can lead to better protection measures for marine life. By staying informed and supporting conservation initiatives, everyone can contribute to safeguarding these magnificent creatures. The next time you hear about a pilot whale stranding, remember the importance of ongoing research and community efforts in addressing this complex issue.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.