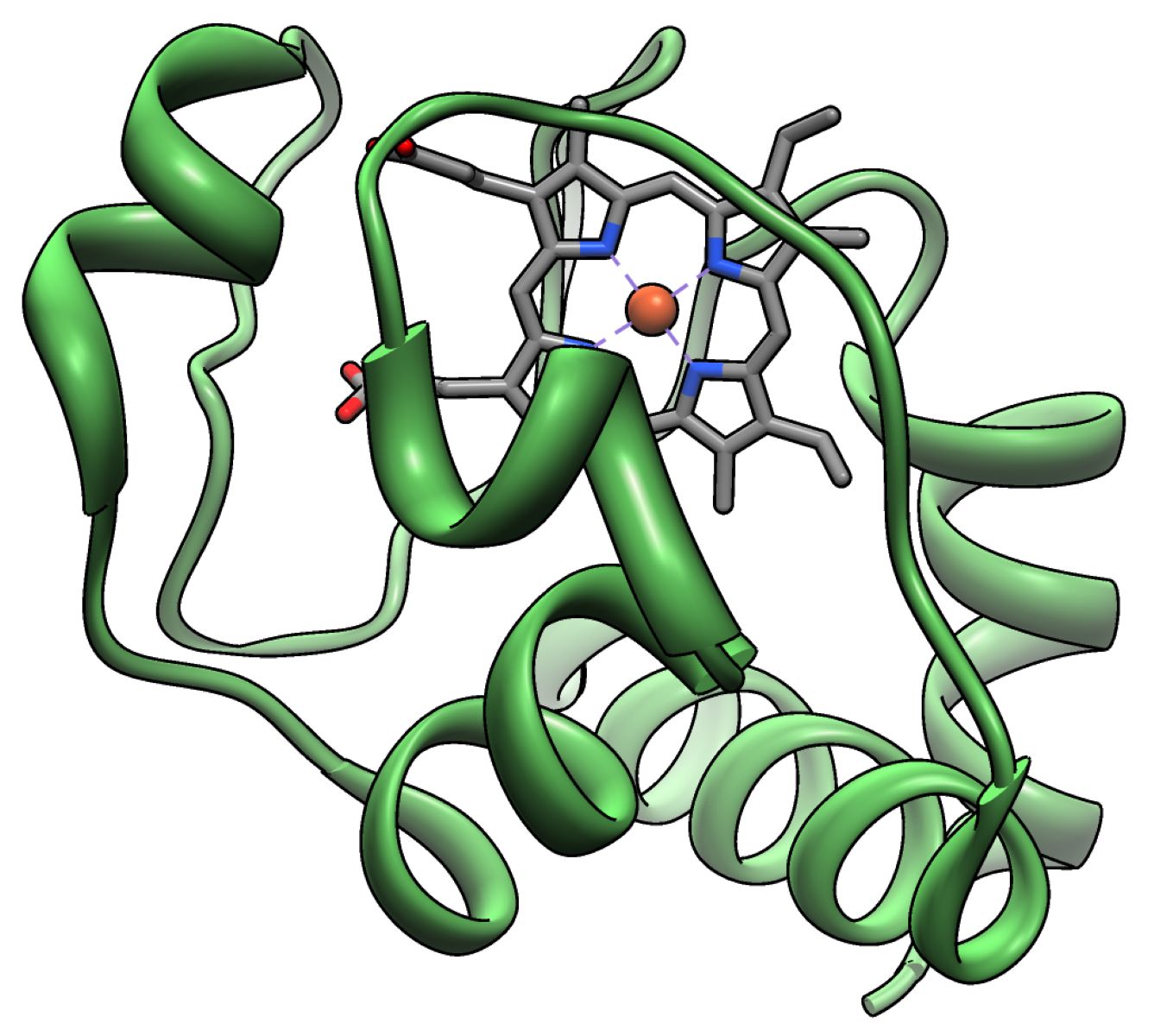
Cytochrome C Peroxidase is a fascinating enzyme that plays a crucial role in cellular respiration. Found in yeast and other organisms, this enzyme helps break down hydrogen peroxide, a potentially harmful byproduct of metabolism. Without it, cells would struggle to manage oxidative stress, leading to damage and dysfunction. This enzyme's structure and function have been extensively studied, revealing insights into how proteins work at a molecular level. From its unique heme group to its interaction with cytochrome c, every aspect of this enzyme offers a glimpse into the intricate world of biochemistry. Ready to dive into 40 intriguing facts about Cytochrome C Peroxidase? Let's get started!
Key Takeaways:
- Cytochrome C Peroxidase is a superhero enzyme that protects cells from harm by breaking down harmful substances and helping generate energy for the cell.
- Research on Cytochrome C Peroxidase could lead to new treatments for diseases and provide insights into aging and cellular processes.
What is Cytochrome C Peroxidase?
Cytochrome C Peroxidase (CCP) is an enzyme found in yeast and other organisms. It plays a crucial role in cellular respiration by helping to break down hydrogen peroxide, a potentially harmful byproduct of metabolism. Here are some fascinating facts about this essential enzyme.
-
CCP is a heme enzyme, meaning it contains a heme group, which is an iron-containing compound that allows the enzyme to carry out its function.
-
The primary function of CCP is to reduce hydrogen peroxide to water, preventing oxidative damage to cells.
-
CCP is found in the mitochondria, the powerhouse of the cell, where it helps maintain cellular health.
-
The enzyme was first discovered in yeast, but it is also present in other eukaryotic organisms.
-
CCP works closely with cytochrome c, another protein involved in the electron transport chain.
Structure and Function of Cytochrome C Peroxidase
Understanding the structure and function of CCP can provide insights into its role in cellular processes. Let's dive into some structural and functional aspects of this enzyme.
-
CCP has a unique three-dimensional structure that allows it to interact with hydrogen peroxide and cytochrome c.
-
The enzyme's active site contains a heme group, which is essential for its catalytic activity.
-
CCP undergoes conformational changes during its catalytic cycle, which are necessary for its function.
-
The enzyme's structure has been studied extensively using techniques like X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy.
-
CCP's activity is regulated by the availability of its substrates, hydrogen peroxide, and cytochrome c.
Cytochrome C Peroxidase in Cellular Respiration
CCP plays a vital role in cellular respiration, a process that generates energy for the cell. Here are some facts about its involvement in this critical process.
-
CCP helps protect cells from oxidative stress by breaking down hydrogen peroxide, a reactive oxygen species.
-
The enzyme is part of the mitochondrial electron transport chain, which is responsible for ATP production.
-
CCP works in tandem with other enzymes and proteins to ensure efficient energy production.
-
The enzyme's activity is crucial for maintaining the balance of reactive oxygen species in the cell.
-
Mutations in the CCP gene can lead to impaired cellular respiration and increased oxidative stress.
Research and Applications of Cytochrome C Peroxidase
Research on CCP has led to a better understanding of its function and potential applications in biotechnology and medicine. Here are some interesting findings and applications.
-
Scientists have engineered CCP variants with altered properties for use in biotechnological applications.
-
CCP has been used as a model system to study protein-protein interactions and electron transfer processes.
-
The enzyme has potential applications in bioremediation, where it could be used to break down environmental pollutants.
-
Researchers are exploring the use of CCP in biosensors for detecting hydrogen peroxide and other reactive oxygen species.
-
Studies on CCP have provided insights into the mechanisms of other heme enzymes and their roles in cellular processes.
Cytochrome C Peroxidase and Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress occurs when there is an imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species and the cell's ability to detoxify them. CCP plays a crucial role in mitigating oxidative stress. Here are some facts about its role in this process.
-
CCP helps prevent oxidative damage to cellular components like DNA, proteins, and lipids.
-
The enzyme's activity is upregulated in response to increased levels of hydrogen peroxide.
-
CCP works in concert with other antioxidant enzymes to protect cells from oxidative stress.
-
The enzyme's role in reducing oxidative stress is essential for maintaining cellular health and preventing diseases.
-
Research on CCP has contributed to our understanding of the mechanisms underlying oxidative stress and its impact on health.
Evolutionary Significance of Cytochrome C Peroxidase
CCP has evolved to perform its function efficiently in different organisms. Here are some facts about its evolutionary significance.
-
The enzyme is highly conserved across different species, indicating its importance in cellular processes.
-
CCP's structure and function have been fine-tuned through evolution to optimize its catalytic activity.
-
Comparative studies of CCP from different organisms have provided insights into the evolution of heme enzymes.
-
The enzyme's evolutionary adaptations have allowed it to function effectively in various cellular environments.
-
Research on CCP has shed light on the evolutionary pressures that have shaped the function of heme enzymes.
Cytochrome C Peroxidase in Disease and Therapy
CCP's role in cellular health makes it a potential target for therapeutic interventions. Here are some facts about its involvement in disease and therapy.
-
Dysregulation of CCP activity has been linked to various diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders and cancer.
-
The enzyme's role in mitigating oxidative stress makes it a potential target for antioxidant therapies.
-
Researchers are exploring the use of CCP inhibitors as potential treatments for diseases associated with oxidative stress.
-
Studies on CCP have provided insights into the mechanisms of drug resistance in cancer cells.
-
The enzyme's activity can be modulated by small molecules, which could be used to develop new therapeutic agents.
Future Directions in Cytochrome C Peroxidase Research
Ongoing research on CCP continues to uncover new aspects of its function and potential applications. Here are some future directions in CCP research.
-
Scientists are investigating the role of CCP in aging and age-related diseases.
-
Research on CCP's interactions with other proteins could lead to new insights into cellular processes.
-
The development of new techniques for studying CCP could provide a deeper understanding of its function.
-
Researchers are exploring the use of CCP in synthetic biology and bioengineering applications.
-
Future studies on CCP could lead to the development of new therapies for diseases associated with oxidative stress.
Final Thoughts on Cytochrome C Peroxidase
Cytochrome C Peroxidase (CCP) plays a crucial role in cellular respiration by breaking down hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen. This enzyme, found in yeast and other organisms, helps protect cells from oxidative damage. CCP's structure, with its heme group, allows it to efficiently catalyze this reaction. Researchers study CCP to understand more about oxidative stress and its link to diseases like cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. By learning about CCP, scientists can develop better treatments and therapies. Understanding CCP also sheds light on the broader field of enzymology and how enzymes work in general. This knowledge can lead to advancements in biotechnology and medicine. Cytochrome C Peroxidase may seem like a small piece of the puzzle, but its impact on health and science is significant. Keep exploring, and who knows what other fascinating facts you'll uncover!
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


