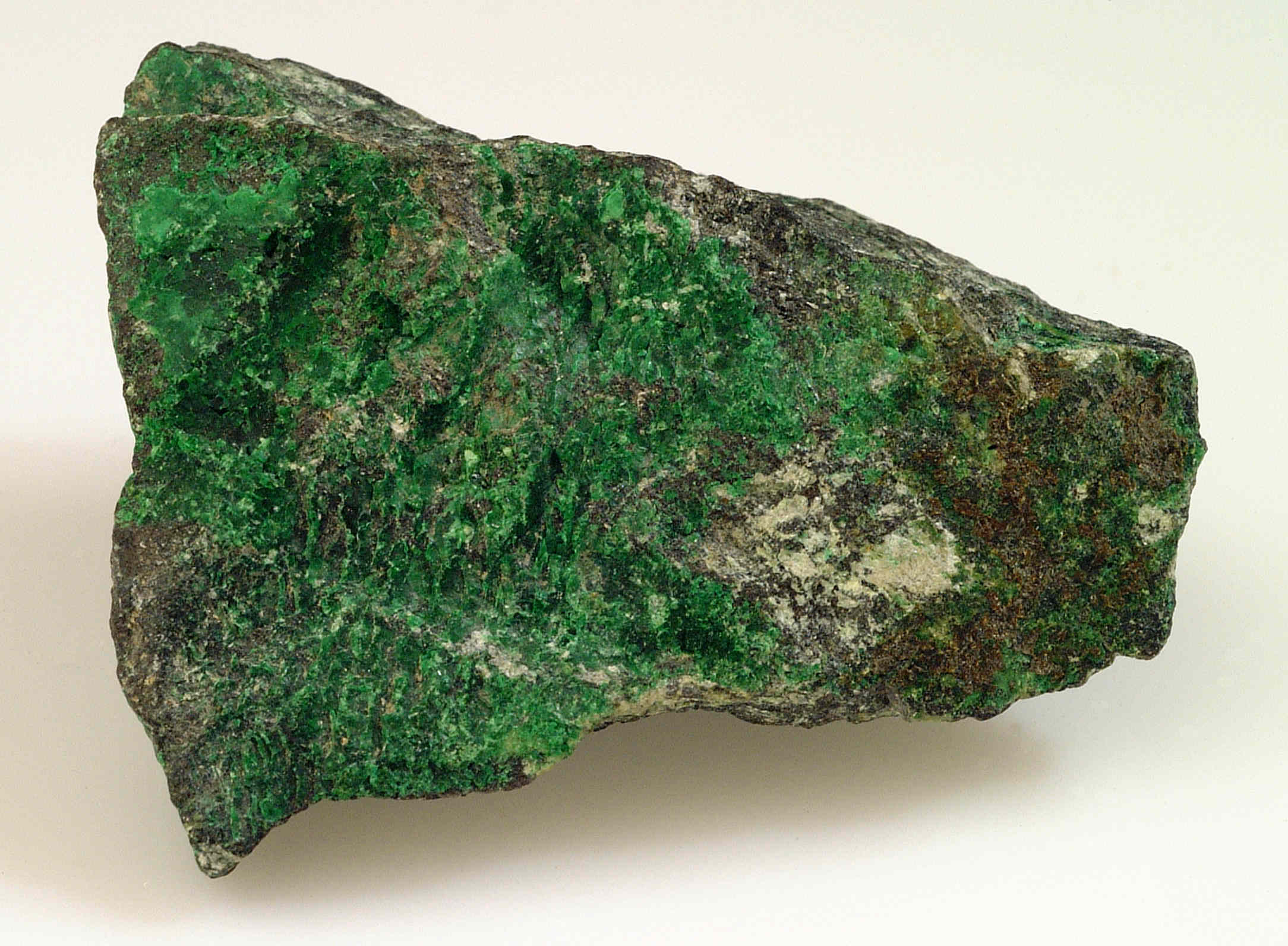
Zaratite is a rare, vibrant green mineral that often catches the eye of geologists and collectors alike. But what makes this mineral so special? Zaratite is a nickel carbonate mineral, typically found in serpentine rocks. Its striking color and unique properties make it a fascinating subject for study. This mineral is not just a pretty face; it has a rich history and intriguing formation process. From its discovery to its various uses, Zaratite offers a glimpse into the Earth's geological wonders. Ready to learn more? Here are 30 facts that will deepen your understanding of this captivating mineral.
Key Takeaways:
- Zaratite is a rare, vibrant green mineral with unique properties. It's primarily collected for its beauty and used in jewelry and educational settings. It's sensitive to acids and dehydration, so it requires careful preservation.
- Zaratite, named after a Spanish diplomat, forms in specific geological settings like nickel-rich deposits. It's found in locations such as New Caledonia and the Ural Mountains. Collectors should handle and store it with care to maintain its beauty.
What is Zaratite?
Zaratite is a rare mineral that captures the interest of geologists and collectors alike. This vibrant green mineral has a unique composition and fascinating properties. Let's dive into some intriguing facts about Zaratite.
-
Zaratite is a nickel carbonate mineral with the chemical formula Ni3(CO3)(OH)4·4H2O.
-
It was first discovered in 1851 by the Spanish mineralogist Andrés Manuel del Río.
-
The mineral is named after the Spanish diplomat Don Lucas de Zaraté, who was a patron of del Río.
-
Zaratite typically forms in the oxidation zones of nickel-rich deposits.
-
It is often found in association with other nickel minerals like garnierite and annabergite.
Physical Properties of Zaratite
Understanding the physical properties of Zaratite helps in identifying and differentiating it from other minerals. Here are some key characteristics.
-
Zaratite has a bright green to emerald green color, making it visually striking.
-
It has a vitreous to silky luster, giving it a shiny appearance.
-
The mineral has a Mohs hardness of 3 to 3.5, which means it is relatively soft.
-
Zaratite exhibits a perfect cleavage in one direction, which refers to how it breaks along specific planes.
-
It has a specific gravity of 2.6 to 2.8, indicating its density compared to water.
Occurrence and Locations
Zaratite is not commonly found everywhere. Its occurrence is limited to specific geological settings. Here are some notable locations.
-
Significant deposits of Zaratite have been found in New Caledonia, a French territory in the Pacific Ocean.
-
It is also found in the nickel mines of Riddle, Oregon, in the United States.
-
Zaratite has been discovered in the Ural Mountains of Russia, a region known for its rich mineral diversity.
-
In Spain, Zaratite occurs in the nickel mines of the province of León.
-
The mineral is also present in the nickel-rich laterite deposits of Western Australia.
Uses and Applications
Although Zaratite is not widely used in industrial applications, it has some interesting uses. Here are a few.
-
Zaratite is primarily collected by mineral enthusiasts and geologists for its rarity and beauty.
-
It is sometimes used as a minor ore of nickel, although its contribution is minimal compared to other nickel minerals.
-
The vibrant green color of Zaratite makes it a popular specimen in mineral collections and museums.
-
Some jewelers use Zaratite in custom jewelry pieces, although its softness limits its use.
-
Zaratite can be used in educational settings to teach students about mineralogy and geology.
Interesting Facts About Zaratite
Beyond its basic properties and uses, Zaratite has some fascinating aspects that make it unique. Here are a few more interesting facts.
-
Zaratite often forms as crusts or botryoidal (grape-like) aggregates on other minerals.
-
The mineral can alter to other nickel minerals over time, such as garnierite.
-
Zaratite is sensitive to acids and can dissolve in hydrochloric acid, releasing carbon dioxide gas.
-
It can also dehydrate when exposed to dry air, losing its water content and altering its appearance.
-
The bright green color of Zaratite is due to the presence of nickel ions in its structure.
Collecting and Preserving Zaratite
For those interested in collecting Zaratite, there are some tips to ensure its preservation. Here are some important considerations.
-
Zaratite specimens should be stored in a cool, humid environment to prevent dehydration.
-
Handling Zaratite with care is essential due to its softness and perfect cleavage.
-
Cleaning Zaratite should be done with water and a soft brush to avoid damage.
-
Labeling Zaratite specimens with their location and date of collection adds value to the collection.
-
Joining mineral clubs or online forums can provide valuable information and resources for Zaratite collectors.
The Final Word on Zaratite
Zaratite, a rare and captivating mineral, has intrigued geologists and collectors alike. Its vibrant green hue and unique formation process make it a standout in the world of minerals. Found primarily in nickel-rich environments, zaratite forms through the weathering of nickel sulfides. Despite its beauty, it's not commonly used in jewelry due to its softness and tendency to dehydrate. However, its rarity and striking appearance make it a prized specimen for collectors. Understanding zaratite's properties and origins not only enriches our knowledge of geology but also highlights the intricate processes that shape our planet. Whether you're a seasoned collector or a curious enthusiast, zaratite offers a glimpse into the fascinating world of minerals. So next time you come across this green gem, you'll appreciate the story it tells and the natural wonder it represents.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.