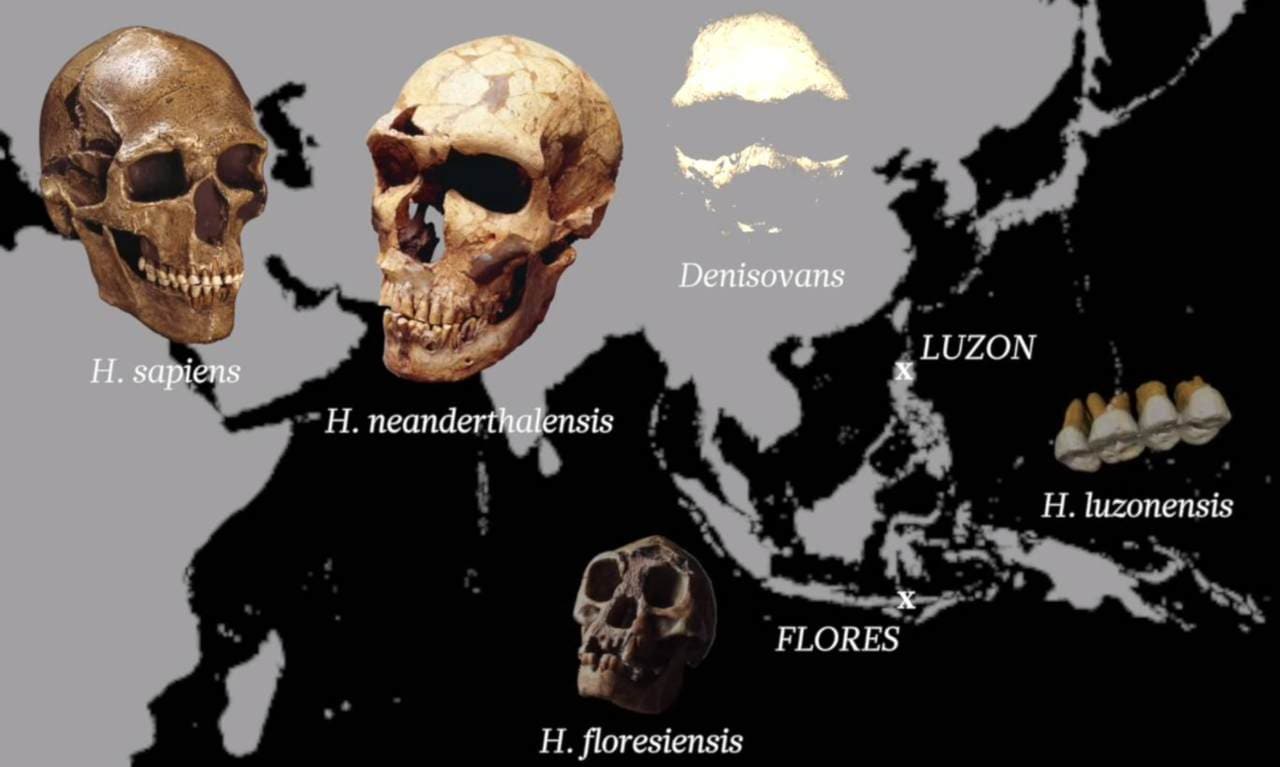
Homo luzonensis is a fascinating addition to the human family tree. Discovered in the Philippines, this ancient species has sparked curiosity and debate among scientists. What makes Homo luzonensis so intriguing? Their unique blend of features. They exhibit a mix of traits seen in both modern humans and much older hominins. This blend suggests a complex evolutionary history. Why should you care? Understanding Homo luzonensis helps us piece together the puzzle of human evolution. It shows that our ancestors were more diverse and widespread than previously thought. Ready to dive into 40 amazing facts about this mysterious species? Let's get started!
Key Takeaways:
- Homo luzonensis, a new human species, was discovered in the Philippines, challenging previous migration theories and adding complexity to the human family tree. Its unique traits highlight the adaptability of ancient humans to different environments.
- The discovery of Homo luzonensis has sparked public interest, inspired documentaries and books, and promoted collaboration among scientists. It serves as a reminder of the rich and diverse history of the human family.
Homo Luzonensis: A New Discovery in Human Evolution
Homo luzonensis is a relatively recent addition to the human family tree. Discovered in the Philippines, this species has sparked interest and curiosity among scientists and the public alike. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about this ancient human relative.
-
Homo luzonensis was discovered in Callao Cave. In 2007, a team of archaeologists found the first remains in Callao Cave on Luzon Island, Philippines.
-
The species was named after Luzon Island. The name "Homo luzonensis" honors the location of its discovery.
-
It was officially classified in 2019. After years of research, scientists officially classified Homo luzonensis as a new species in April 2019.
-
The discovery included teeth and bones. Researchers found seven teeth, two hand bones, three foot bones, and a partial femur.
-
Homo luzonensis lived around 50,000 to 67,000 years ago. Dating techniques suggest these ancient humans roamed Luzon Island during this period.
Physical Characteristics of Homo Luzonensis
Understanding the physical traits of Homo luzonensis helps us learn more about their lifestyle and how they might have lived.
-
They had small teeth. The teeth of Homo luzonensis are smaller than those of other ancient human species.
-
Their molars had unique features. The molars had a mix of primitive and modern traits, making them distinct.
-
Curved toe bones suggest climbing abilities. The curvature of their toe bones indicates they might have been adept climbers.
-
Hand bones were also curved. Similar to their toes, the hand bones suggest climbing was a significant part of their daily activities.
-
They were likely small in stature. Based on the size of the bones, Homo luzonensis individuals were probably shorter than modern humans.
The Significance of the Discovery
The discovery of Homo luzonensis has important implications for our understanding of human evolution and migration.
-
It challenges previous migration theories. The presence of Homo luzonensis in the Philippines suggests early humans might have traveled across Southeast Asia more extensively than previously thought.
-
It adds complexity to the human family tree. Homo luzonensis introduces another branch to the already complex human evolutionary tree.
-
They coexisted with other human species. Evidence suggests Homo luzonensis lived at the same time as other human species like Homo sapiens and Homo floresiensis.
-
It highlights the diversity of ancient humans. The unique traits of Homo luzonensis show the wide range of physical characteristics among ancient human species.
-
The discovery was unexpected. Scientists did not anticipate finding a new human species in the Philippines, making this discovery particularly surprising.
Tools and Lifestyle
Examining the tools and lifestyle of Homo luzonensis provides insights into their daily lives and survival strategies.
-
No tools were found with the remains. Unlike other ancient human sites, no stone tools were discovered alongside Homo luzonensis remains.
-
They might have used organic tools. The absence of stone tools suggests they could have used tools made from organic materials like wood or bone.
-
They lived in a tropical environment. The climate of Luzon Island during their time was tropical, influencing their lifestyle and survival strategies.
-
Homo luzonensis likely hunted and gathered. Based on their physical traits and environment, they were probably hunter-gatherers.
-
They might have used fire. While no direct evidence of fire use was found, it is possible they used fire for cooking and protection.
Genetic and Evolutionary Insights
The genetic and evolutionary aspects of Homo luzonensis offer a deeper understanding of their place in human history.
-
No DNA has been recovered yet. Unfortunately, no genetic material has been extracted from the remains so far.
-
They might share traits with Denisovans. Some scientists speculate that Homo luzonensis could share genetic traits with the Denisovans, another ancient human species.
-
Their origins are still debated. Researchers continue to debate the exact origins and evolutionary path of Homo luzonensis.
-
They might have interbred with other species. It is possible that Homo luzonensis interbred with other human species in the region.
-
Their discovery raises questions about human adaptability. The unique traits of Homo luzonensis highlight the adaptability of ancient humans to different environments.
Future Research and Discoveries
Ongoing research and future discoveries will continue to shed light on Homo luzonensis and their place in human history.
-
More excavations are planned. Archaeologists plan to conduct further excavations in Callao Cave and surrounding areas.
-
New technologies might help. Advances in technology could help uncover more details about Homo luzonensis.
-
Interdisciplinary research is crucial. Combining archaeology, anthropology, and genetics will provide a more comprehensive understanding of this species.
-
Public interest is growing. The discovery of Homo luzonensis has captured the public's imagination, leading to increased interest in human evolution.
-
Educational programs are being developed. Museums and educational institutions are creating programs to teach people about Homo luzonensis and their significance.
Homo Luzonensis in Popular Culture
The discovery of Homo luzonensis has also made its way into popular culture, inspiring various forms of media and public interest.
-
Documentaries have been produced. Several documentaries have been made to explore the discovery and significance of Homo luzonensis.
-
Books and articles have been written. Numerous books and articles discuss the implications of this new human species.
-
They have been featured in exhibitions. Museums around the world have included Homo luzonensis in their exhibitions on human evolution.
-
Educational videos are available online. Many educational videos about Homo luzonensis can be found on platforms like YouTube.
-
They have sparked debates. The discovery has led to debates among scientists and enthusiasts about human evolution and migration.
The Broader Impact on Human Evolution Studies
The discovery of Homo luzonensis has broader implications for the study of human evolution, prompting new questions and research directions.
-
It highlights the importance of Southeast Asia. The discovery underscores the significance of Southeast Asia in human evolution studies.
-
It encourages re-examination of other sites. Researchers are re-examining other archaeological sites in the region for potential new discoveries.
-
It promotes collaboration among scientists. The discovery has fostered collaboration among scientists from different fields and countries.
-
It inspires young scientists. The excitement surrounding Homo luzonensis inspires the next generation of scientists to pursue careers in archaeology and anthropology.
-
It reminds us of our shared history. Homo luzonensis serves as a reminder of the rich and diverse history of the human family.
Final Thoughts on Homo Luzonensis
Homo Luzonensis adds a fascinating chapter to human history. Discovered in the Philippines, this ancient human species lived around 50,000 to 67,000 years ago. Their unique features, like curved toe bones and small teeth, suggest they adapted to their environment in ways different from other early humans. This discovery challenges previous ideas about human evolution and migration patterns.
Understanding Homo Luzonensis helps scientists piece together the complex puzzle of our ancestry. It shows that human evolution wasn't a straight line but a branching tree with many different species. Each new find like this one brings us closer to understanding where we come from.
So, next time you think about human history, remember Homo Luzonensis. Their story is a reminder of how much there is still to learn about our past. Keep an eye out for more discoveries that could change what we know about human evolution.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.